University Directory


A CL student has to complete 131 credit hours in four years to be able to acquire a Bachelor in Law Degree. Law courses are especially designed to assist students in acquiring knowledge of diverse legal areas, so that their career opportunities would be increased to cover both government and private sectors.
After graduating from UBT’s College of Law, students should have a good grasp of the relevant subjects, as well as the necessary skills of transferring and applying their knowledge in the real world..
A CL student has to complete 131 credit hours in four years to be able to acquire a Bachelor in Law Degree. Law courses are especially designed to assist students in acquiring knowledge of diverse legal areas, so that their career opportunities would be increased to cover both government and private sectors.
After graduating from UBT’s College of Law, students should have a good grasp of the relevant subjects, as well as the necessary skills of transferring and applying their knowledge in the real world..


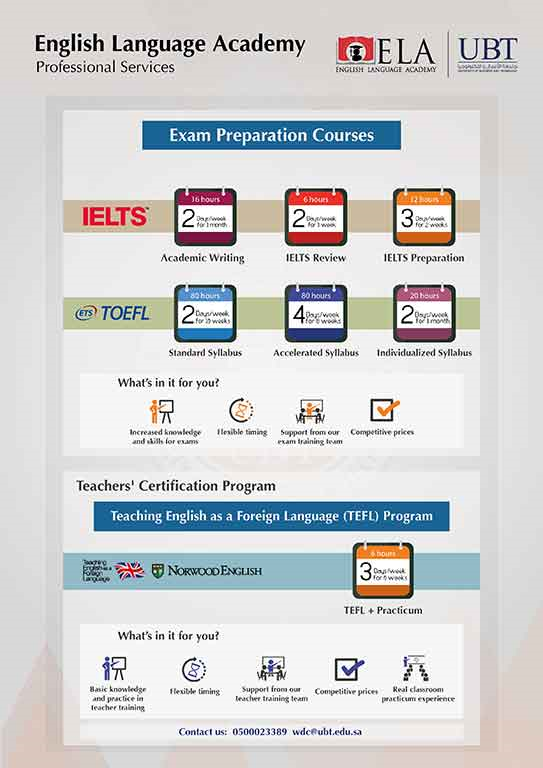
ELA was established to offer students a unique opportunity to learn English. In today’s global job market, being able to speak English is a huge asset. The ELA will not only help students master the English language, but will also equip them with the critical thinking skills and communication skills employers look for.

UBT’s English Language Academy’s four level intensive English language course is an integrated-skills and content-based program that develops students’ proficiency in English. The entire course is delivered in four modules. Each module spans eight academic weeks at a rate of 25 hours per week.
The program utilizes Cengage’s LIFE American edition series’ textbooks which adopt a communicative approach emphasizing language learning in real life contexts, and the production of language in a broad range of speaking and writing situations – thereby mirroring the functional descriptors of the CEFR.
| Levels | Textbook | CEFR | Course Duration | Hours per week |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Cengage Life 1 | A1 | 8 weeks | 25 |
| Level 2 | Cengage Life 2 | A2 | 8 weeks | 25 |
| Level 3 | Cengage Life 3 | B1 | 8 weeks | 25 |
| Level 4 | Cengage Life 4 | B1+ | 8 weeks | 25 |
Upon admission to UBT, students sit the online Oxford Placement Test (OPT) to ensure placement in their proper level. Accurate placement of students is essential for success in their English studies.
The entire four session program takes students from the Beginner Level (A1) up to the Upper Intermediate (B2). ELA ensures that these are reliable and accurate language proficiency standards by correlating ELA levels to internationally accepted proficiency benchmarks.

The grading system used is as follows:

ELA adopts CEFR (Common European Framework of Reference for Language Learning) international standards in structuring its English Language Program. CEFR is highly reliable and provides a basis for mutual recognition of language qualifications around the globe, thus facilitating educational and occupational mobility.
This framework consists of the following:
A1: Refers to the student’s basic ability to communicate and exchange information in a simple way.
A2: Refers to the student’s ability to deal with simple, straightforward information and begin to express oneself in familiar contexts.
B1: Refers to the student’s ability to express oneself in a limited way in familiar situations and to deal in a general way with non-routine information.
B1+: Refers to the student’s ability to enter unprepared into conversation on familiar topics, express personal opinions and exchange information on topics that are familiar, of personal interest or pertinent to everyday life.
B2: Refers to the student’s capacity to achieve most goals and express oneself on a range of topics. A student can understand the main ideas of complex text on both concrete and abstract topics, including technical discussions in his/her field of specialization.
C1: Refers to a student’s ability to communicate with emphasis on how well it is done, in terms of appropriacy, sensitivity and the capacity to deal with unfamiliar topics.

Communicative reading Strategies for students:
Pre-reading:
Pre-reading tasks are adopted to activate students’ schematic knowledge of what they are about to read (based on their pre-existing knowledge) as this knowledge will help them understand the text. When reading, students are using their pre-existing knowledge to predict content. In class, predictions are communicated to partners.
During Reading:
Reading is done in pairs or collaboratively to promote greater interactions among students.
Post-reading:
Students tell each other about what they have read and engage in:
Active Communication (speaking):
Students are encouraged to:
The aim for most students is fluency. ELA develops fluency through pair work and group work speaking activities by providing interesting discussion topics that offer students something to talk about.
Communicative Writing:
Writing, like all other aspects of language, is communicative. ELA Students are required to write e-mails, SMS messages, lists, notes, cover letters, reports, proposals, memos, assignments, essays, etc. Students engage in doing research projects, publishing blogs, and creating individual and group profiles.

Admission to the ELA is processed through UBT’s Admission Office, as the ELA is the gateway to UBT. All applicants must follow UBT’s admission procedures. Kindly check the following link:
[Click Here]
Students who do not meet the English language proficiency requirements for admission to UBT are admitted automatically to the ELA.
Online admission steps:
Note:

ELA utilizes a battery of standardized tests designed to measure students’ English language proficiency and academic English ability, to ensure accurate placement of students in its four level English language program; and to determine whether their English is adequate for full-time study at UBT.
A test schedule is announced online (UBT Website) and the Admission Office, at the end of each session and during registration week. Each student is given a UBT ID which he/ she has to present at the ELA exam center on the placement test date, in addition to his/ her Saudi national ID, Passport, or Iqama.
ELA’s Placement Tests include:


In addition to the administration of the IELTS exam on its premises, ELA is an international Pearson VUE Authorized Testing Center. The Pearson VUE Prometric Test Center at ELA is part of Pearson VUE computer–based assessment services. Pearson is a global leader in electronic testing for information technology, academic, government and professional clients, providing a full suite of services from test development to data management.
Most Common Exams at Pearson VUE Test Center are:

The ELA has instituted the English for Specific Purposes (ESP) program to provide a preparation course intended for students as well as employees in the market place who wish to develop their professional skills in the English Language, and who need development in communication, organizational behavior and leadership skills.


The TOEFL, IELTS, GMAT, and SAT Preparation courses are six-week intensive study courses that develop a student’s test-taking skills for each exam. The programs focus on:

ELA Student education goes beyond the coursework. Extracurricular activities form a vital part of ELA students’ experience - creating unique opportunities for friendship and learning. Students can engage and participate in an array of activities on campus that include:
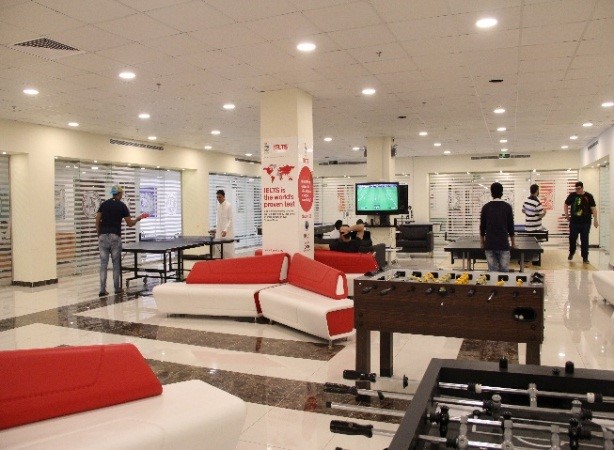
ELA Students Recreational Hall (Dahban):
ELA has an in-house Recreational Hall available to students all day long. Sports include billiards, table tennis, PS4, Football and more.
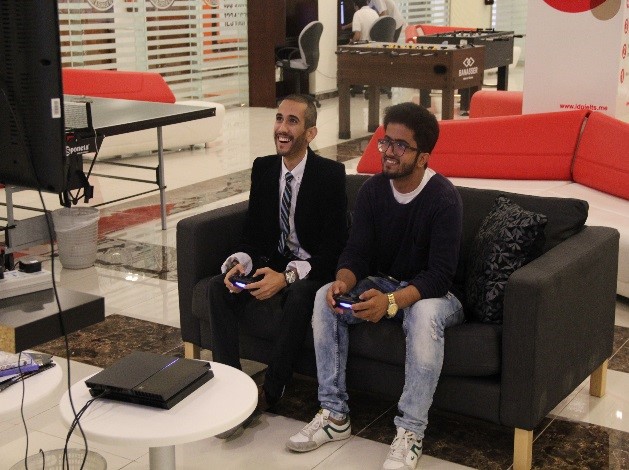


Fitness & Wellness Athletic Activities
ELA students have access to UBT’s overall fitness and wellness facilities. These facilities provide opportunities for students to exercise, manage stress, and stay healthy. They are convenient for students on campus and membership is free.
The facilities include gym, weight lifting, and lockers. There are also basketball courts, an indoor pool, a volleyball court, bowling alleys, snooker, billiards, and much more.


ELA encourages students to actively join extracurricular activities on Campus, including clubs.
1- Arts &Crafts Club:
This club aims to enhance students’ creativity through art exhibitions and workshops. Students express themselves artistically through drawing, painting and handcrafting, practicing their cognitive skills and creativity in a relaxed environment.


2- Fitness and Health Club:
This club aims to increase students’ physical activity by providing them with all facilities in the gym. Students have access to UBT facilities. The club sponsors training sessions, basketball, and volleyball games.
3- Social Activity Club:
This club aims to increase students’ physical activity by providing them with all facilities in the gym. Students have access to UBT facilities. The club sponsors training sessions, basketball, and volleyball games.

ELA’s Males Campus is located in Dahban, while the Females Campus is located at Sari in Jeddah. Dahban campus is located on a sprawling 4725 square meters of land and has its own state-of-the-art building, fully furnished with 30 classrooms, two fully equipped computer labs, and administrative facilities. Classrooms are equipped with state-of-the-art educational technology – ranging from smart boards and sound systems, to highly configured computers.



ELA provides thoughtful services for special needs students. Students with special needs are furnished with accommodation plans that cater for their needs making sure they have access to quality education in coordination with student learning support center and their relevant teachers.

IT services are provided to ELA Male and Female Campuses with IT support for administrative, academic, and quality assurance operations throughout the year. Specifically, the following services are extended to ELA faculty & personnel:
Computers:
ELA provides computer facilities, software, resources and IT service to students, staff and Teachers. All classrooms are equipped with high performance desktop computers with genuine Microsoft Windows 10, User friendly Smart Board and Projector, and all the classroom-presentation-tool & software’s required for teaching purposes. This enhances the teaching and learning environment by allowing teachers, staff, and students to incorporate various types of media in the classroom.
Computer Labs:
Dhahban ELA has two computer Labs computers. Both are equipped with high performance PC’s with headphones. Microsoft Windows 10 and MS Office 365 are being used as the latest, flexible and updated software. Numerous learning applications are installed on computer lab PC’s for students’ learning purposes. The labs are also equipped with printers. ELA provides computer lab facilities for on-campus and online-learning student use. Students are allowed to access Internet or e-mail, to prepare word documents, projects, class assignments or to use other course software that is relevant to teaching at ELA.
E-Service:
Printing Services:
Printing service is provided through network Connection. IT supervisor assists teachers, staff and students with their printing needs.
Maintenance Services:
The IT support specialist provides IT maintenance in all computer labs, classrooms and administrative offices.
Opera system:
Opera is UBT’s own customized e-system; it is the main academic system used by students, faculty members and staff. It is a set of all sort of different internal applications. It combines course registration, grading, Opera online, attendance, and students’ portal. Listed below are some details.
a) Opera Admissions and Registration:
This system allows various registration and admission tasks such as calendar, admitting new students, fulfilling admission requirements and more. It involves course registration tasks such as add, drop, swap, etc.
b) Opera Students affairs:
Opera Student affairs system keeps tracks of student’s affairs activities; and monitors students, events, extra credits, activities, etc.
c) Opera Attendance:
Opera attendance allows faculty members to take the attendance of all students inside the classroom. It informs instructors about students registered in their courses, and also keeps track of their daily attendance. Faculty members have access to Opera attendance on campus, or off campus through the use of Remote Apps service. Students can keep track of their attendance and view it through Opera Online.
d) Opera Online (student’s portal):
Opera Online is the main student’s portal for accessing his/her Opera related information – e.g., registration, grades and attendance. It allows students to go online to access their academic system information – allowing them to register online for their courses; view and edit their own personal records; view their grades, study plan, transcripts, acknowledgement letter and financial statements.
Moodle: Modular Object- Oriented Dynamic Learning Environment
Moodle is the open source web-based learning management system used at UBT. It is the main communication link between instructors and their students. Each registered student will have his/her course listed each academic term in Moodle. Instructors are able to use Moodle to post course materials such as presentations, handouts, projects and are able to communicate with their students using messages, chat and discussion forums. They can also assess students by administering quizzes and assignments, and using other tools.
McGraw-Hill Campus:
McGraw-Hill Campus is a Book resources tool provided by McGraw-Hill to our campuses though integration with Moodle. Students can access the customized book and the customized e-learning platform and have access to quizzes and exercises provided by the instructor.





We are a team that work together to implement the student affairs goals, mostly young professionals working in the student affairs to gain more knowledge and experience they work together as a family under a wise and great supervision.


If you are experiencing any difficulties that might negatively affect your life or academic performance, make sure to utilize counseling service in campus.
What counselor can provide to students?
Contact To meet with our counselor, please visit with the student counseling unit or send an Email to scu@ubt.edu.sa . It is located in the student’s affairs building. The office hours from 8:30 A.M till 4:30 P.M

The Student Council Unit represents the students’ entity and determines a link between the students and the university administration. This unit serves students, discuss their issues, and raise their inner voices by defending their points of view. It also aims to promote active and cooperative spirits between students on one-hand and the management and faculty members on the other hand, developing awareness of moral values and infuse the spirit of responsible leadership in them. The council consists of fifteen number of students, presidents and vice president. This council selects its members through an election process in accordance with the deanships standards.

This unit takes leading efforts allowing students to translate and apply what they have learned to the surrounding community and take an action in problem solving processes. It is also facilitate many volunteering opportunities for students through the volunteering club to help them finish their required 100 volunteering hours.

The media office seeks to promote the programs, activities and services provided by the deanship, and endorse media communication between employees of the university professors, and administrators, and students, in addition its monitor and document all activities and events of deanship through the newspapers and social media channels.

Unit of innovation and entrepreneurship:
This unit has two main sections.

Everything starts with an idea; it could be a significant invention or innovative idea that can be turned into a successful business. The unit of innovation and entrepreneurship help students of the University of Business and Technology and directing them to the proper steps that contribute to shape their ideas and turn them into reality.


This unit works to encourage and improve talented students’ ability and develop their creativity, where the work of this section to discuss and explore the talents of the students and highlighted through them to share their talents in domestic and foreign forums.
This unit oversees the following clubs:
If you have an idea or a creative project, do not hesitate to communicate with the unit director.

UBT students can enjoy a variety of clubs and organizations that interest a wide range of students who are actively involved on campus. Membership in most of these clubs and groups is open to all UBT registered students.

Academic Clubs:
Talents and Art Clubs:

The Deanship of Scientific Research was established in 2013 as a Research and Consultation Center at the University of Business and Technology. Through the implementation of new strategies, hard work, and dedication the Center evolved into a Deanship in 2017. As a result, UBT was able to transform from a teaching-based university to a teaching and research-based university promoting scientific innovation and research.
The Deanship of Scientific Research supports UBT's research mission and solve problems facing the business sector and the whole economy in Saudi Arabia and the region, in line with Saudi Vision 2030 and the Development Plan 2020. The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) has a strategic goal; to become one of the advanced countries in science, technology and innovation by (2030) as well as creating a “knowledge-based economy and society” UBT and DSR works to fulfill this goal.
On this note, The Deanship brings together faculty members, staff, and students, unifying their efforts to develop interdisciplinary approaches to goal-oriented problems. DSR, through its Research Development Department, Economic Development Department, Publication Department, and Consultancy services link researchers and the industry together, providing an opportunity to solve current issues facing the Saudi community and economy, improve current materials, or develop new ones. Moreover, DSR looks for the industrial potential that will support the economic development of the kingdom through startups and economic development projects.


The research flagship is an interdisciplinary research group covering researches in Agriculture and food, Water treatment, Energy conversion and storage, Electronics and Communication and IT, Transport and Automotive, Construction and building, and Health from the business, legal, science, technology, and advertising point of view – serving the axes of economic development. Registering your research interest will guarantee you better opportunities by connecting you to many researchers who are exploring your area of interest from different perspectives. Moreover, coordinating research efforts will take UBT a step closer towards operating the research roadmap effectively – thereby, contributing to economic development and serving the community.




UBT Library: Online catalogue
http://library.ubt.edu.sa/uhtbin/cgisirsi.exe/?ps=SG2OPYSYXd/MAIN/219150007/60/502/X
UBT Library: Databases
http://ubt.edu.sa/Library/Databases
Application Forms and policies
Flagships Application Forms
https://goo.gl/forms/AifvVsT09sjdXgEv1
Technology Transfer
Research
Research Funding
Scientific chair
Research reward
Publication Fees
Data Collection, Processing, and Analysis
Technology Transfer
Intellectual Property
Business and Entrepreneurship Hospital
Book
“A written work on sheets of paper or bound together a front and back cover”
https://goo.gl/forms/3bdM0iZGEsYXFg2I2
Book chapter
“A main division of a book with a separate title”
https://goo.gl/forms/RiQUGTxrE64k9B8k2
Conference proceedings
“A paper that has been presented at a conference, and then collected by the conference itself to be published in a volume called conference proceeding”
https://goo.gl/forms/VyqGcIcEfMVYZQ9h1
Paper
“An article that has been published in a journal”
https://goo.gl/forms/iFPxuUVhHeuxA7DN2
Participation in conferences
“An individual paper presented at a conference”
https://goo.gl/forms/paR4YXLvob4CtVVA3
Patent
“An exclusive right granted to the inventor/writer to protect its invention/writing from being sold, reused, copied, etc.”
https://goo.gl/forms/Zmu25qTj97s0kOm72
Graphical Illustration
Verification, Proofreading, and Translation
Consultation
KAUST Core Labs
Core Labs are a prominent feature of the interdisciplinary research ecosystem at the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology.
Core Labs provide state-of-the-art facilities, training and services to the KAUST research community, collaborators and industrial partners. These centrally organized, shared-user facilities provide direct access to specialized research equipment, operated by expert staff with advanced degrees in science and engineering. The Core Labs consists of ten laboratories that are strategically located throughout the academic campus enabling users to transition between labs in a matter of minutes.
https: //corelabs.kaust.edu.sa/
KACST
The King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST) is a scientific government institution that supports and enhances scientific applied research. It coordinates the activities of government institutions and scientific research centers in accordance with the requirements of the development of the Kingdom. It also cooperates with the relevant authorities in identifying national priorities and policies in technology and science, so as to build a scientific and technological basis that serves development in agriculture, industry, mining, etc. It also aims at developing national competences and recruiting highly qualified specialists to help develop and control modern technology in order to serve development in the Kingdom. KACST comprises all the requirements of scientific research, such as laboratories, means of communications, information sources and all necessary facilities.
For general inquirers Email: dsr@ubt.edu.sa

Aiming to support the research process, the University of Business and Technology organizes many research workshops through the Deanship of Scientific Research. The deanship caters to:
List of workshops




The University of Business and Technology has transitioned from a teaching-based institution to a teaching and research-based one. UBT generates knowledge and conducts interdisciplinary quality research that contributes to the economic development and serves the community. Hence, the Deanship of Scientific Research created the Research Roadmap announced in March 2017. The Research Roadmap brings together faculty, staff, and students from across colleges and departments to develop interdisciplinary approaches to goal-oriented problems and industrial potential to support the economy and the society. It is a way of collaboration and organization, uniting all efforts to address current problems affecting the community. The Research Roadmap is an innovative one-of-a-kind effective plan that will take the research in UBT to the next level.
|
DEADLINE FOR SUBMISSION : |
|
|
|
|
Research open day -TBC
|
Dates to Remember |
|
DEADLINE FOR SUBMISSION : |
|
The University of Business and Technology – aiming to support the research process – has collaborated with a number of agencies that will fund the innovative research projects of faculty and staff.!
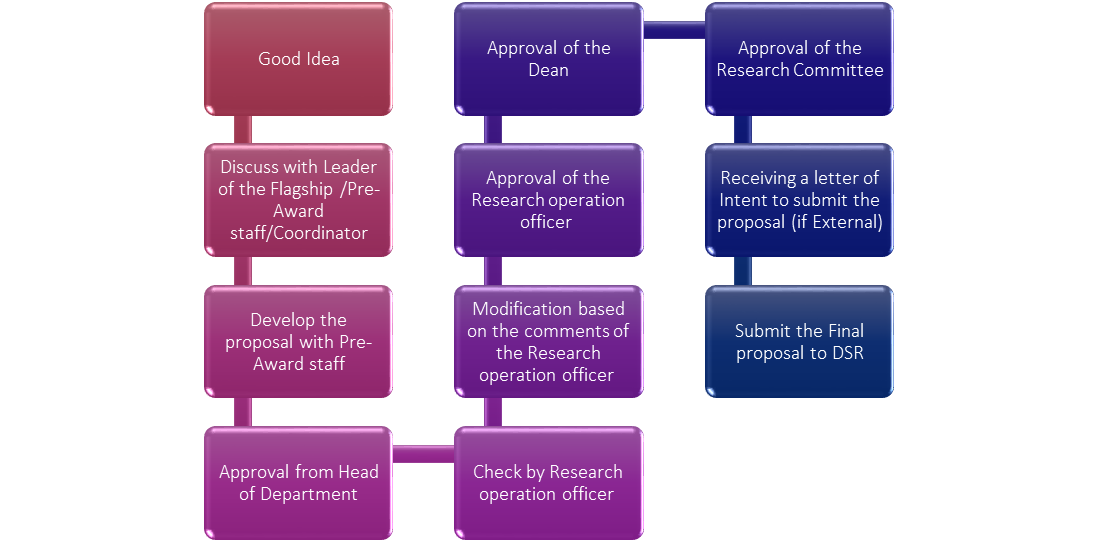
The Funded Research Unit provides support to researchers in all stages of the funding process, through its Pre-Award, Award, and Post-Award offices. The Pre-Award Office will provide the following services:
The University of Business and Technology – aiming to support the research process – funds many innovative research projects of faculty and staff.
Research in Progress
|
Faculty name |
Title |
Abstract |
|
Ali El Rashidi
|
Optical absorption enhancement for A-SI:H Solar Cells using Plasmonic Nanoparticles |
Solar energy is the most favored renewable energy that can be harvested and converted to usable electrical energy using solar cells with a drawback of limited efficiency. The light harvesting and power conversion efficiency can be boosted utilizing nanostructured materials, including nanowires, quantum dots, plasmonic materials, and Nano antennas. In this work, we propose a new structure for an excitonic solar cell with improved light harvesting and power conversion efficiency using plasmonic nanoparticles distributed on the top surface of a conical shaped solar cell. Different metals will be used as plasmonic nanoparticles such as gold, copper, silver and vanadium dioxide. Hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cells which have very strong absorbers using n-type, intrinsic, and p-type layers will by used. Therefore only a very thin film is required to capture most of the incident light. These light absorbing molecules can also be deposited with solution processable techniques. This means that large area devices can be manufactured using simple and cheap manufacturing processes. Hence, these solar cells are relatively cheap to produce; and can be prepared as flexible devices. The flexible and lightweight nature of these cells means they are more portable than traditional solar cells and can be incorporated more easily into consumer goods, such as backpacks. Another advantage of the strong absorption properties of these types of solar cells is they perform well under low or diffuse light conditions and so can be used indoors. On the other hand, conical shape of PIN is used to enhance the light trapping by multiple reflections of incident light. The optimum shape, size and position of plasmonic materials and optimum shape and height of the PIN conical shape will be determined using a finite difference time domain (FDTD) simulation tool. According to the parametric study, we will fabricate a prototype for a solar cell that can be industrialized. Electrical and optical properties of the proposed model will be determined and verified with the ones obtained by the parametric study as well. |
|
Faculty name |
Title |
Abstract |
|
Hussein Reda |
Assessment of quality cost in Saudi Arabia manufacturing industry |
Quality costs are those resulting from producing, identifying, repairing, and avoiding defective products. It consists of the following four categories: 1) Internal failure costs are incurred prior to the products delivery to the customer. They include costs of scrap, rework, retest, downtime, yield losses or disposition. 2) External failure costs occur after the products are delivered to the customer. They include categories such as complaint adjustment, returned products, warranty charges, and liability or allowances concessions. 3) Appraisal costs result from measuring, evaluating, and auditing material and products to determine their conformance to specifications. They include costs of inspection and testing of incoming materials, through production, testing, and equipment calibration. 4) Preventive costs are associated with activities aimed at reducing appraisal and failure costs. They include costs of quality planning and design, new products review, process control, training, quality data analysis and reporting, and improvement projects. A survey of several manufacturing industries in Saudi Arabia will be conducted. The survey includes a cross representation of manufacturing activities existing in the region. They include construction material, light metal fabrication, plastics and glass products, and assembly of various electric & mechanical products and home appliances. The survey is intended to assess the level of awareness and quantitative estimates of quality costs as related to the above four categories. The survey design and findings will be presented along with analysis. Specific conclusions will be drawn regarding quality costs studies and reduction/improvements programs as related to the surveyed industry categories. |
|
Seoud Abouamer
|
Piezoelectric for lighting highways |
Sound is a regular mechanical vibration that travels through matter as a waveform. Longitudinal sound waves – compression waves – transmitted through the ambient air are made up of waves of alternating pressure deviations from the equilibrium pressure, causing local regions of compression and rarefaction. In This work, different intensity of the input sound was used. Compared with other mechanical energy sources, it is very difficult to use mechanical energy from sound in order to generate electrical energy using a conventional PZT-based bulk or thin film piezoelectric energy harvester." To overcome this difficulty, the team worked with zinc oxide nanowires, a piezoelectric nanomaterial that leads to a much more sensitively response |
|
Samer Bali
|
Novel design and implementation of Chip-less tag using radio frequency identification (RFID) system |
Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) wireless technology is becoming the most popular and important instrument that is used in many applications such as logistic chains, tracking and localization items. RFID has the capability to read the items without needing line of sight. In addition, RFID is used for applications that require relatively long reading distance compared to the traditional barcode system. The main obstacle of the RFID system is the cost of an active tag unit as well as a passive tag unit with chip, and this still prevents RFID from being a widely used identification system. Chip-less tag is one solution to effectively reduce the cost of the tag. However, this solution imposes new challenges in RFID systems. One of the main classical challenges is the development of anti-collision methodologies in order to identify multiple tags simultaneously. The anti-collision protocols that are frequently used in traditional active and passive RFID tags with chips are not suitable for chip-less tags, since chip-less tags do not have any on board controlling element (chip) or circuit. Therefore, new anti-collision protocols should be developed for chip-less tags. In this project we will design a microstrip printed antenna using an Ink-Jet printer in our lab at the University of Business and Technology. In this research project, it is intended to design and develop new chip-less tags that should be extremely cheap. The new tags will need the development of new protocols for reading multiple tags simultaneously. As a result, this will open the way for building an initial prototype of an enhanced passive RFID system. |
|
Faculty name |
Title |
Abstract |
|
Elsayed Elfar
|
Modeling and Implementation of Grid Connected Hybrid Wind/Spv System and Application for Saudi Site |
The shortage of fuel resources worldwide has required urgent search for alternative energy sources to meet up present day demands. Solar and wind energy sources is a clean, unfailing and environment-friendly potential resource among all renewable energy options. At present, there is a need for continuous supply of energy, which cannot be satisfied - due to seasonal and periodic variations – solely by a wind energy system or solar photovoltaic system. Hybrid PV/battery bank/utility grid system (PV/BB/UG) is considered as a basic solution for any shortage of fuel resources worldwide. The overall cost of such hybrid system is the main issue that should be studied deeply before installation of the system. This research introduces a complete study of the performance of a hybrid PV/BB/UG system. The cost of kilo Watt of each individual source has been calculated and the kWh cost of the overall PV/BB/UG İs calculated as well taking into consideration the installation and running cost. The introduced system is simulating on a real load of a building at the University of Business and Technology located in Dahban, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Finally, we used our study in lighting some labs in the same engineering building. It is generally agreed that using local information such as generated power from PV array and state of battery change are calculated using computer program under known insolation and load demand. The optimal power management is carried out using the designed program which has been tried and tested using actual data – under different operational conditions. Matlab-Simulink is used for carrying out a simulation using daily data of the load demand, insolation and temperature of Jeddah site, KSA. The results obtained show the beneficially of the hybrid integrated system
|
|
Ali Elrashidi
|
Simulating Ultra-Sensitive Gas Sensors Using Plasmonic Nanostructures |
Gas sensors are important for a myriad of applications including petroleum production, automotive industry, agriculture, and environmental studies. Excellent gas sensors should be ultra-sensitive, selective, cheap, simple, energy efficient, feasible, fast in response, and can be used for a wide range of applications. Furthermore, the general architecture of the sensor should remain constant even if sensing materials or detected gases are changed. Unfortunately, the reported techniques in the literature partially have the characteristics of ideal gas sensors. As a result, we propose to use the finite difference time domain (FDTD) method to simulate gas sensor designed by using plasmonic gold nanoparticles and gas sensitive polymeric materials. We plan to monitor only one physical quantity that will be changed in all chemical reactions between sensitive polymers and gases. Therefore, the basic structure of our proposed sensor will be fixed and only the sensitive polymeric materials can be changed. In addition, the proposed method will have the same advantages of traditional polymeric gas sensors but with extra sensitivity improvement. Also, the proposed sensor can be simulated above flat surfaces or optical fibers which widen its applications area.
|
|
Mahmood Ali
|
A framework to evaluate the state of food retail supply chain in Saudi Arabia |
Supply Chain Management has been playing a key role in food retail business in developed countries by providing various segments of customers with quality products in a highly efficient manner. The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) is following the lead of developed countries, with rapid growth trend in super and hypermarkets. However, the role of supply chain management and its impact on meeting customer needs are not well understood because of lack of readily available data. There is need to develop an appropriate framework for the KSA food retail sector to study the impacts of the various elements of the supply chain. This paper describes a framework that researchers can utilize to study the supply chain impacts on the food retail sector. |
|
Ahmad Shawqi
|
Fabrication Of A Microelectrode Array, First Generation, Glucose Biosensor- PHASE I |
The worldwide market for bio and chemical sensors is large, being valued at $13 billion in 2011, and growing quickly with a projected compound annual growth rate of 9.6% between 2011 and 2016. Many of these sensors are amperometric, where the concentration of a chemical analytic (e.g., free available chlorine, ozone, glucose) is determined by measuring the diffusion limited current at an electrode. Fabricating such microelectrode arrays in a cheap and efficient manner is a technological challenge that has not been fully solved (please see Literature Review), as demonstrated by the low usage of these electrodes in commercial amperometric sensors. The researchers will build on work completed in the University of Limerick to first construct a microelectrode array, first generation, glucose biosensor and then similar sensors for other analytics. |
|
Ahmad Shawqi
|
Preparation of Hybrid Composite Materials And Their Microwave Properties Applied on The Telecommunication Towers In Jeddah – Proof of Concept |
The extensive development of telecommunication systems and electronic devices has raised the electromagnetic pollution to a level never attained before. This has led to environmental questions, health concerns and a wide variety of applications. This justifies an active quest for novel and effective electromagnetic material creation that could provide solutions for the microwave behavior. Thus, materials with high efficiency to diminish electromagnetic interferences pollution have become a mainstream field of research. The present project will focus on the preparation, fabrication and development of hybrid composite materials to reduce the electromagnetic pollution that is produced by the telecommunication towers in Jeddah. These materials are expected to act as a barrier, absorber, or reflector of the electromagnetic radiation. Protection of humans and other biological objects from the harmful action of the electromagnetic waves will therefore be achieved. These materials are expected to be implemented in different applications – i.e. antenna techniques and production, military applications, and improving the electromagnetic compatibility between different electronic devices.
|
|
Isam Al jawarneh
|
Design of a Data Warehouse Model for Decision Support in Higher Education: A Case study at the University of Business & Technology (UBT) |
The goal of this study is to design a Data Warehouse (D W) dimensional model at the University of Business and Technology (UBT). UBT is striving to be a world-class university. For this purpose several Information Systems (IS) were developed such as
|
|
Ahmad Shawqi
|
Flame spray Drying Synthesis of Calcium Phosphate Nanoparticles |
The investigators propose to study the synthesis of calcium phosphate nanoparticles using the flame spray pyrolysis technique. Calcium phosphate salts are important biomaterials and flame spray pyrolysis is a fundamentally important technique extensively used in industry for the formation of metal oxide
|
|
Wesam Habib
|
Empirical Asset Pricing Saudi Stylized Facts and Evidence |
I estimate proxy specifications of (Fama and French, 2014) five-factor model to produce stylized facts of the Saudi capital market and test an APT model. The data set is the panel of all publicly traded firms, excluding financial and negative book value of equity firms. My contribution to the extant literature is three-fold: [1] organizing Saudi market data based on beta and firm-specific fundamentals, namely, growth, size, accounting earnings, and equity investments, [2] conducting a parsimony analysis within the theoretical framework of Merton's (1973) APT, and [3] quantifying the information risk facing marginal investor by decomposing earnings into cash flows and accruals; and investigating respective loadings in an unrestricted version of the parsimonious specification. Proxy asset pricing specifications, though intuitively appealing, are scant due to lack of theoretical frameworks and misguided significance tests of factor loadings. Throughout, I address this issue in detail and keep the empirical analysis under describing market facts and testing an APT model.
|
UBT collaborates with many organizations and universities to provide all support for the scientific research process. Organizations that fund research are:
KACST is a scientific government institution that supports and enhances scientific applied research. It coordinates the activities of government institutions and scientific research centers in accordance with the requirements of the development of the Kingdom through the following programs:
Strategic Technologies of fundamental Research Support Program:
The program aims at developing high-quality long-term fundamental research. This strategic step is part of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia’s quest towards achieving a higher rank among Middle East countries.
Research Grants Programs:
Seeking to support scientific research in all fields, the city has introduced a number of research grants programs that provide financial, as well as technical support for researchers and students who enroll in human and applied sciences.
Innovative Research Support Program:
The innovative research support programs aim at improving the economic variables in the Kingdom by developing research aimed at achieving specific goals in specific fields.
Erasmus Mundus is a cooperation and mobility program in the field of higher education that aims to enhance the quality of European higher education; and to promote dialogue and understanding between people and cultures through cooperation with Third-Countries. In addition, it contributes to the development of human resources and the international cooperation capacity of Higher education institutions in Third Countries by increasing mobility between the European Union and these countries.
The Gulf Science Innovation and Knowledge Program (GSIKE), is a part of the UK Government's strategy to support a long-term relationship between academia in the UK and the Gulf.
The call is funded by the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS), the department that brings together responsibilities for business, industrial strategy, science, innovation, energy, and climate change.
The United Kingdom’s International Organization for Cultural Relations and Educational Opportunities. The British Council managed this call of proposal. The GSIKE Program priority areas include:
Please, click on the link below to download the research Policies & Procedures:
[Click here]
Please, click on the link below to download the research Policies & Procedures:
[Click here]
UBT Faculty and staff show interest in research and are publishing all year-round.
Scientific Journal
Aiming to support the research process, the University of Business and Technology strives to secure scientific chairs. A Scientific chair is a financial grant provided by individuals or organizations to support scientific research. The Scientific Chair is currently under process.
Policies and procedures
Apply
Current
In progress
This is a reference to all that includes all UBT researchers and their research interests
The Research Statement is a way that allows researchers to express their research interest, which opens doors of opportunities and allows for more room for collaborative research and innovation.
The Research and Consultation Center produced a documentary about research and the research process in collaboration with researchers from different UBT colleges. Enjoy watching, hoping you find your inspiration in their stories:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g250jnbH3GA
The Journal Club is an opportunity for all professionals:
The club includes the following seminars:
Both students and faculty members participate in leading discussions of the papers. Furthermore, it brings to campus prominent external speakers to ensure their research expertise is conveyed to UBT faculty.



Scientific Café, managed by RCC and RCC college Coordinators, is a monthly event that takes place in a casual setting –e.g., in coffee houses, a local library, or a faculty lounge – after work to meet a prominent scientist in a special scientific field and hear him provide an informal (no PowerPoint) introduction to an interesting current scientific topic, that presents the theme of the month. Scientific Cafés are also open to students.
The Research Symposium is an annual event that showcases research in the university, presents published and ongoing research in each college – offering opportunities for UBT researchers to meet; discuss ideas; share knowledge; and get feedback. Researchers present their ideas on posters; and the best poster from each college wins the Best Poster Presentation award.
The University of Business and Technology hosted the 3rd Research Symposium Poster session, an annual event to showcase the research in the university, present published and ongoing research in each college, and to offer opportunities for UBT researchers to meet, discuss ideas, share knowledge and get feedback. This year, there were 10 posters from CBA, 17 from CE, and 4 from JCA. And for the first time ELA researchers participated with 2 posters.
The posters were evaluated by 8 jury members from all colleges. The winners of the Best Poster Award were: Dr. Zulfeequar Alam from CBA; Dr. Ahmad Barham from CE; Mr. Saleh Al-Takrouri from JCA; and Ms. Asmaa Hakami from the ELA.
The Deanship of Scientific Research, organizer of this event, took this opportunity to stress the importance of scientific research. DSR Dean Dr. Basma El Zein encouraged researchers to conduct more research, and to publish in peer-reviewed journals to lift the university’s ranking to be among the top international universities, known for scientific and applied research, and to serve Vision 2030. Working towards this goal, UBT has signed many MOUs with universities in the US and Europe. Many research projects are already in progress. Moreover, UBT has partnered with the international academic publishing company Springer Nature to improve the quality of research in the university.
To Download PDF: Book of Abstract : Book of Poster
The Deanship of Scientific Research at the University of Business and Technology organized the 2nd Research Symposium on Wednesday April 29, 2017 in the Library building of Dhahban Campus under the patronage of Prof. Hussein Al Alawi, the Rector of UBT. The aim of this event was to promote the concept of scientific research and to contribute towards the cultural development of Saudi Arabian society.
Faculty members of all departments at the University of Business and Technology presented their research results on 32 posters. The poster presentations were arranged in three sessions: CBA, CEIT and JCA session – taking into account different criteria, such as quality, originality and significance of research; as well as the quality of presentation. The jury chose the best four posters and winners of the best poster award are: Majed Al-sharayri and Arif Mohamed from CBA; Mohammad Ahmad Kanan from CE; and Haneen Shoaib from JCA.
The event was a great success. It received positive comments from pleased guests, faculty, and students.
To Download PDF: Book of Abstract + Book of poster
The Research and Consultation Center of University of Business and Technology organized the 1st Research Symposium on Wednesday 30th of March 2016 in the Library building of Dhahban Campus. The aim of this event was to promote the concept of scientific research and to contribute to the cultural development of Saudi Arabian society.
Prof. Hussein Al Alawi, the Rector of UBT, welcomed all participants and gave the opening address – emphasizing the important role of Research in academic institutions and encouraging all faculty members to conduct applied research. Prof. Al Alawi mentioned that this event was a UBT RESEARCH FESTIVAL. After that, Dr. Basma EL Zein, the Director of RCC gave a speech about the role of the RCC in contributing to UBT’s vision of converting Saudi Arabia into a knowledge-based economy and society, where researchers from different disciplines would join in their efforts to solve real work problems that contribute to the economic development of the Kingdom and the region; and serve the society. She focused as well on the Center’s goals, activities, and services. Dr. El Zein also presented the 6 research flagships – namely, Water Treatment, Energy Conversion and Storage; Electronics and Communication; Transportation and Automotive research; Construction and Buildings; and Health, where research has to be conducted from different perspectives. She also discussed technological business and advertising.
Faculty members of all departments of the University of Business and Technology presented their research results on 44 posters. The poster presentations were divided into three sessions: CBA, CEIT and JCA session. Taking into account different criteria, such as quality, originality and significance of research and the quality of presentation, the jury chose the best six posters. In addition, this event was an opportunity to commend Dr. Ayman Zerban as the Researcher of the month for his research efforts and his research contributions to UBT. The event was a great success; and received positive comments from pleased guests, faculty, and students.
To Download PDF: CBA Book of abstract : CE Book of abstract : JCA Book of abstract : CBA Book of poster : CE Book of poster : CBA Book of poster
Welcome to the Industry Partnership Unit where we create collaboration between the University of Business and Technology and industries. To facilitate this, a program called the Industry Membership Program was created. The Industry Membership Program was designed to promote communication between academia and industries in order to facilitate the transfer of knowledge to industies.
Based on membership fees, this program provides an opportunity for an industry to contribute to academia specifically through research, consultancy, scientific chairs, careers and many other areas of interest.
Members receive a membership package including many services from UBT such as:
The Industry Membership Program will serve UBT by:
Pros for a collaboration between the University and Industries:
For the University:
For the Industry:
Guide for a successful partnership:
| Memberships; | UBT offers | |||
|
|
Platinum |
Gold |
Silver |
Bronze |
|
Booth on the University Campus |
Booth 4m² |
Booth 1m² |
Poster |
Poster |
|
Facilities to promote the company at UBT |
✓ |
✓ |
||
|
Booth on career day |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Access to senior students (PhD / Ms / Post doc) and Alumni DataBase for employment |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Invitation to UBT Industrial Day |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Access to attend workshops |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
|
Visibility of their name and logo |
✓ |
✓ |
||
|
Overview of the R&D work done |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Access to UBT Labs |
✓ |
|||
|
Propose research projects to UBT for the company |
Open |
Up to 7 |
Up to 2 |
1 |
|
Access to seed fund program, start-up and spin-off opportunities |
✓ |
|||
|
Access to interns |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Opportunity to join pilot project initiatives as a prelude to commercialization |
✓ |
✓ |
||
|
Consultancy projects |
Open |
Up to 7 |
Up to 2 |
1 |
|
Visibility of the company on graduation day |
✓ |
|||
|
Discounts for UBT symposia, colloquia, and seminars |
✓ |
✓ |
||
|
Membership in the Advisory College board |
✓ |
|||
|
Membership Fees (in SAR) |
2,000,000 |
1,000,000 |
500,000 |
200,000 |
The innovation unit provides support in obtaining patents and in technology transfer.
The Patent & Technology Transfer is responsible for:
Process:

|
# |
Student group |
|
|
Abstract |
|
|
1 |
Eng. Fares Osama Sukhairi and Eng. Mansour Mohammed Qawas
|
Cooling Wave |
|
An innovative Electric appliance, a rapid cooling wave technology because it provides speed in cooling and high It is similar to the microwave oven in heating the aliments, rapid way. It can be used in hospitals, labs, restaurants
|
|
|
2 |
Eng. Gaith Nader Anwar Edrees and Eng. Siraj Muneer Almirawi
|
VertTile |
|
Energy harvesting using nanomaterials provides an opportunity Sustainable systems, or Self-powered systems, are a new the need for external power source like batteries or such. us such as mechanical vibrations, noise, and/or human movement of our invention is the transformation of massively electricity. The electricity generated can either be stored device. From street lamps, street lights, traffic posts, warning plugs for phone charging, and more. The application possibility
|
|
|
3 |
Ms. Noha Obaid |
Drawer’s Safe-closing Tool |
|
Drawers have been used since the forties but it never witnessed significant improvements. Ever since children have been getting hurt by drawers either by closing them on their fingers or while reaching for dangerous objects inside of them, such as chemical detergents or sharp objects. For adults, it is obvious that when closing a drawer, they should push it inside with keeping their fingers away from the edges. But with children aged from 8 months to 36 months it’s not that clear for them. They can exert an enough amount of force that can cause severe pain if it is closed on their little fingers. So it is our sincere duty to come up with innovative yet simple ideas to secure our children away from harmful incidents. I have made two tools that can solve these types of problems, the first is to minimize the pressure on fingers if the fingers were inside while the closing process and the second tool is to completely lock the drawer.
|
|
|
4 |
Eng. Malaz Marwan Alidelbi, Eng. Loay Osama Abuahmed |
Outdoor Smart Parking System using Image Processing and Li-Fi Communication Technology |
|
Recently many new technologies have been developed that help in solving the parking problems to a great extent the traffic generated by cars searching for parking spaces takes up to 40% of the total traffic, with a huge impact on the mobility and quality of life of residents.
|
|
|
5 |
Eng. Malaz Marwan Alidelbi, Eng. Loay Osama Abuahmed |
NetLight |
|
An emergency lighting system includes an input, a charging circuit, an auxiliary power supply, a plurality of lights, a driver, and a controller. The input is configured to receive line voltage. The charging circuit is configured to receive the line voltage and output a charging voltage. The auxiliary power supply is configured to receive the charging voltage. The plurality of lights includes a first group of lights and a second group of lights. The driver is configured to provide power to the plurality of lights Wireless mesh networks (WMNs) have attracted increasing attention and deployment as a high- performance and low-cost solution to last-mile broadband internet access. WMNs have been broadly accepted in the conventional application sectors of ad hoc networks because of their advantages over other wireless networks. Traffic routing has a critical role in determining the performance of wireless mesh networks. Routing protocol design for wireless mesh networks is Critical to maintaining the performance and reliability of wireless mesh networks. Thus a routing protocol or an algorithm for WMNs should be carefully designed taking into account the specific characteristics of that network. |
|
Under the Patronage of Dr. Abdullah Dahlan, every year UBT celebrates its students’ innovations and achievements, encouraging more creativity.
|
year |
Student group |
project title |
scientific illustration |
Abstract |
|
2017/2018
|
Ms. Noha Obaid |
Drawer’s Safe-closing Tool |
|
Drawers have been used since the forties but it never witnessed significant improvements. Ever since children have been getting hurt by drawers either by closing them on their fingers or while reaching for dangerous objects inside of them, such as chemical detergents or sharp objects. For adults, it is obvious that when closing a drawer, they should push it inside with keeping their fingers away from the edges. But with children aged from 8 months to 36 months it’s not that clear for them. They can exert an enough amount of force that can cause severe pain if it is closed on their little fingers. So it is our sincere duty to come up with innovative yet simple ideas to secure our children away from harmful incidents. I have made two tools that can solve these types of problems, the first is to minimize the pressure on fingers if the fingers were inside while the closing process and the second tool is to completely lock the drawer. |
|
2017/2018
|
Eng. Malaz Marwan Alidelbi, Eng. Loay Osama Abuahmed |
Outdoor Smart Parking System using Image Processing and Li-Fi Communication Technology |
|
Recently many new technologies have been developed that help in solving the parking problems to a great extent the traffic generated by cars searching for parking spaces takes up to 40% of the total traffic, with a huge impact on the mobility and quality of life of residents. |
|
2016/ 2017 |
Eng. Fares Osama Sukhairi and Eng. Mansour Mohammed Qawas
|
Cooling Wave |
|
|
|
2016/ 2017 |
Eng. Gaith Nader Anwar Edrees and Eng. Siraj Muneer Almirawi
|
VertTile |
|
|
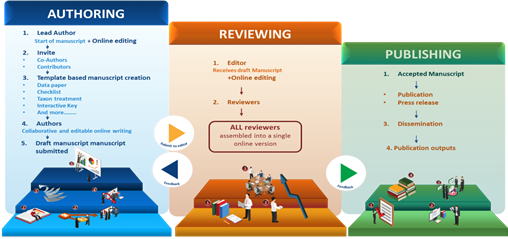
The scientific journal is an annual publication, gathering all publications (journal articles, research papers, conference proceedings, book chapters, etc.) by faculty members and staff throughout the year:
UBT Scientific Journal 2018.
Download (Click here)
UBT Scientific Journal 2017.
Download (Click here)
UBT Scientific Journal 2016
Download (Click here)
Image Register your publication:
Book
“A written work on sheets of paper or bound together a front and back cover”
https://goo.gl/forms/3bdM0iZGEsYXFg2I2
Book chapter
“A main division of a book with a separate title”
https://goo.gl/forms/RiQUGTxrE64k9B8k2
Conference proceedings
“A paper that has been presented at a conference, and then collected by the conference itself to be published in a volume called conference proceeding”
https://goo.gl/forms/VyqGcIcEfMVYZQ9h1
Paper
“An article that has been published in a journal”
https://goo.gl/forms/iFPxuUVhHeuxA7DN2
Participation in conferences
“An individual paper presented at a conference”
https://goo.gl/forms/paR4YXLvob4CtVVA3
Patent
“An exclusive right granted to the inventor/writer to protect its invention/writing from being sold, reused, copied, etc.”
https://goo.gl/forms/Zmu25qTj97s0kOm72
The Deanship of Scientific Research is delighted to represent all research activities at UBT, highlighting the research work of UBT faculty members and students, their publications, their inventions, and their awards. Researcher of the month, seminars, workshops, visits, announcements for coming events will be also included in the E-Newsletter.
Enjoy reading, and wishing you more publications, inventions, conferences, awards, citations, etc.
2019:
E-newsletter Volume 4, Issue 1
Download (Click here)
2018:
E-newsletter Volume 3, Issue 3
Download (Click here)
E-newsletter Volume 3, Issue 2
Download (Click here)
E-newsletter Volume 3, Issue 1
Download (Click here)
2017:
E-newsletter Volume 2, Issue 3
Download (Click here)
E-newsletter Volume 2, Issue 2
Download (Click here)
E-newsletter Volume 2, Issue 1
Download (Click here)
2016:
E-newsletter Volume 1, Issue 3
Download (Click here)
E-newsletter Volume 1, Issue 2
Download (Click here)
E-newsletter Volume 1, Issue 1
Download (Click here)
The UBT Times magazine is dedicated to all members of UBT. It aim is to inform about every college/department achievement, highlight students’ experiences and success, showcase accomplishments, and motivate all members to further success. Enjoy reading, and wishing you more celebrations, collaborations, media coverage, etc.
Send us your news
https://docs.google.com/forms/d/1Wlb32ISHamD2uQ_o-_GLz9603lcAzsfBxAabueQ6LX0/edit
2018: TBC
The Consultancy Services Unit will put UBT experts in support of the community to contribute to the rapid development in the world of knowledge as a link between theory and practice.
UBT has high caliber faculty, and expert consultants to provide advice, verify, and assess, etc. in all disciplines. UBT staff and faculty develop systems, processes, campaigns, etc. for specific types of Projects requested by our clients, organize specific workshops, training, and research, etc. in all areas.
Policies
NA
For companies:
NA
For individuals:
NA
For UBT faculty members who wishe to provide consultancy services for industries, please click this link:
https://goo.gl/forms/npeZZMzbgKkjVAv73
Current
In progress


Graduate Honors record not available...

Graduate Honors record not available...

Graduate Honors record not available...

Graduate Honors record not available...

Graduate Honors record not available...

Graduate Honors record not available...

UBT Preparatory Program consists of non credited courses specifically designed to improve student's proficiency in English before they undertake undergraduate study and to develop and to improve student's knowledge of mathematical and analytic techniques through the medium of English Language
The program also familiarizes students with various majors available at the college, the requirements of undergraduate study and discipline in all forms. The program consist of the following courses:
At first, the newly admitted student should take an English assessment test to determine his/her language skill level. Each student will be positioned according to his/her test result to the following list:
| COURSE | UNITS | PREREQUISITE |
|---|---|---|
| Academic English Level 2 | 1 | English Language - Level 1 |
| Academic English Level 3 | 1 | Academic English Level 2 |
| Academic English Level 4 | 1 | Academic English Level 3 |
| College Level English I | 4 | Academic English Level 4 |
| College Level English Ii | 4 | College Level English I |
Students might be exempted from taking any courses at ELA by submitting one of the following options:

It is highly important to follow the program plan during different semesters, as they are designed to prepare the students in each stage of the program. It is crucial for the student to meet his/ her academic advisor and follow the study plan of his/her major closely. This would typically include taking the lower level courses in the first and second year, getting as much of the general education as possible, and then moving to take the major courses and possibly some minor courses. This is a very carefully structured process that students should closely adhere to.

It is highly important to follow the program plan during different semesters, as they are designed to prepare the students in each stage of the program. It is crucial for the student to meet his/ her academic advisor and follow the study plan of his/her major closely. This would typically include taking the lower level courses in the first and second year, getting as much of the general education as possible, and then moving to take the major courses and possibly some minor courses. This is a very carefully structured process that students should closely adhere to.

It is highly important to follow the program plan during different semesters, as they are designed to prepare the students in each stage of the program. It is crucial for the student to meet his/ her academic advisor and follow the study plan of his/her major closely. This would typically include taking the lower level courses in the first and second year, getting as much of the general education as possible, and then moving to take the major courses and possibly some minor courses. This is a very carefully structured process that students should closely adhere to.

Below are courses description for Advertising Communication plan

Below are courses description for Advertising Creative Design courses

Graduates will become competitive in many public and private sector advertising and advertising related roles and, as proven in the previous years, they will be ready to work in:

Below are courses description for Advertising Management plan

Graduates will become competitive in many public and private sector advertising and advertising related roles and, as proven in the previous years, they will be ready to work in:

Below are courses description for Advertising Creative Design plan

Graduates will become competitive in many public and private sector advertising and advertising related roles and and, as proven in the previous years, they will be ready to work in:

In order to prepare for our MBA Program, it would be helpful to have taken classes in finance, financial analysis, accounting, statistics, research methods, management and economics. The number of courses required from this category differs from an applicant to another according to the degree of relevance of his or her education and area of expertise to the field of Business Administration.
| The Pre-MBA Course |
|---|
| Principles of Accounting |
| Principles of Economics |
| Principles of Finance |
| Principles of Management |
| Introduction to Management Information Systems |
| Introduction to Quantitative Business Analysis |
There are two options to acquire a degree from this program. The first is to acquire an MBA degree in General Business Administration by earning 48 credit hours of the available courses without any area of concentration. The second option is to acquire an MBA degree with one of the available 8 areas of concentration by earning 48 credit hours divided into 36 credit hours of core courses and 12 credit hours of the area of concentration or option.

MBA Program The MBA program is a 48-credit curriculum that offers a comprehensive framework for providing knowledge, tools and skills of entrepreneurship and initiative ability of today’s business leaders to manage business organizations in an increasingly competitive business environment.
It is offered as a masteral degree in General Management or a degree with options in Accounting, Finance, Human Resource Management, International Business Administration, Marketing and Supply & Operations Management, Management Information System.
The MBA program with options is structured around the two interrelated course structures: 36 credit hours of core courses and 12 credit hours of option courses. The MBA general management program is structured with 36 credit hours of core courses and 12 credit hours of mixed courses of choice.
Core Courses: (12 Courses, 36 credit hours) Regardless of the MBA option, all students are required to complete the following courses:
| 1 | FIN 511 | Financial Management | 3 Credit Hours |
| 2 | ACCT 512 | Managerial Accounting | 3 Credit Hours |
| 3 | HRM 511 | Organizational Behavior | 3 Credit Hours |
| 4 | MIS 511 | Management Information System | 3 Credit Hours |
| 5 | ECON 511 | Managerial Economics | 3 Credit Hours |
| 6 | MKT 511 | Marketing Management | 3 Credit Hours |
| 7 | MGT 511 | Advanced Quantitative Business Analysis | 3 Credit Hours |
| 8 | IBM 511 | International Business Management | 3 Credit Hours |
| 9 | EPR 511 | Entrepreneurship | 3 Credit Hours |
| 10 | OPM 511 | Operations Management | 3 Credit Hours |
| 11 | HRM 512 | Human Resource Management | 3 Credit Hours |
| 12 | MGT 581 | Business Strategies | 3 Credit Hours |

This section of the program is carefully designed to accommodate MBA seekers, who come from non-business background. The fact that such students need a kind of survival kit that helps them to cope with their peers who come from business background or hold an undergraduate degree in business related discipline. This kit is the Pre-MBA program, which comprises 6 courses, 1-credit each and will be offered in one semester. Applicants who have accredited background in one or more of these courses may get a waiver on case-to-case basis.
| Pre-MBA Course List | |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Quantitative Business Analysis | 1 credit |
| Principles of Accounting | 1 credit |
| Principles of Finance | 1 credit |
| Principles of Economics | 1 credit |
| Introduction to Management Information Systems | 1 credit |
| Principles of Management | 1 credit |
| 1- MGT 499 – Introduction to Quantitative Business Analysis | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
Quantitative Business Analysis is a required course designed to prepare MBA students with a set of tools to meet the challenges of today’s business environment. This course is about statistics and basic modeling for management decisions.
It covers various topical areas spanning from descriptive statistics to inferential statistics and introduction to mathematical programming.
The objectives are:
| 2- ACCT 499 – Principles of Accounting | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
The aim of this course is to familiarize students with the essential accounting system terminologies and functions.In this course, students review accounting reports and methods. The course focuses on the preparation of financial statements.
Emphasis is placed also on the interpretation and use of financial statements for decision making as well as steps of accounting cycle.
| 3- FIN 499 - Principles of Finance | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
This course aims to set the basic financial background that supports the financial knowledge and skills needed for studying MBA courses.
Course topics will cover the basics of financial management and financial markets and institutions.
In addition, teaching the accounting and financial statements and how to use them in evaluating the firm’s financial performance are included. Furthermore, the course will focus on the concepts of the time value of many and the meanings and measures of risk and return.
| 4- Econ 499 – Principles of Economics | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
This course aims to set the basic economic background that supports the economic knowledge and skills needed for studying MBA courses.
Microeconomics concepts will cover demand, supply and equilibrium in addition to elasticity and consumer theory. Microeconomics will focus too, on the theory of the firm, competition and monopoly. The student will learn about wages, interest, rent and profit as returns of the economic factors.
Macroeconomics will cover the national income accounting and determination, unemployment, inflation, money and banking and public expenditure and finance. Macroeconomics will focus too, on international trade and protection, the balance of payment and exchange rates in addition to the concepts of managing the economy.
| 5- BUS 499 – Principles of Management | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
This course focuses on the key managerial functions: planning, organizing, staffing, directing and controlling. Particular emphasis is given to design and development of organizations, marketing decisions, and labor management relations, financing decisions, management theory and role of management information system. The course also introduces students to the main functions of enterprise as well as business environment. Ethics and Social responsibility are also addressed.
| 5- MIS 499 – Introduction to Management Information System | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
This course is an introduction to information systems and information technology for students who are or who will become business professionals in the fast changing business world of today. The focus is helping students learn how to use and manage information technologies to revitalize business process, improve business decision making and gain competitive advantages. There is a major emphasis on the essential role of internet technologies in providing a platform for business, commerce and collaboration process among all business stakeholders in today has networked enterprises and global markets.

| 1- MGT 511 – Advanced Quantitative Business Analysis | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This management course has the primary purpose to introduced advanced modeling techniques used in operations management. Students will learn how to use models such as principles of probability theory and statistics, regression analysis, linear programming, simulation, and other appropriate models to solve practical decision problems utilizing computer software available for the models.
| 2- ECON 511 - Managerial Economics | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course includes the development of basic economic concepts and their application to managerial decision-making. Major topics include Demand and Cost Analysis, forecasting, Pricing Decision, Capital Budgeting and Capital Management, And Decision-Making under Conditions of Risk and Uncertainty.
Pre-requisite: ACCT 531
| 3- EPR 511 - Entrepreneurship | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This interdisciplinary course focuses on all aspects of starting a new business with emphasis on the critical role of recognizing and creating opportunities. Topics include Attributes of Entrepreneurs and Entrepreneurial Careers, Evaluating Opportunities, Writing Business Plan, and Venture Financing.
| 4- MGT 518 – Business Strategies | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This capstone course investigates the methods and techniques used to formulate competitive strategy through the analysis of industries, competitive dynamics, the general management process, and the achievement of sustainable competitive advantage. Students will also be exposed to growth strategies comparative management, impact of taxation, technology strategies; product development and new market strategies. The course heavily emphasizes the use of case studies and in-class simulations. Pre-requisite: Econ 511, Fin 511, MKT 511, MIS 511 & OPM 511

In addition to the Core Course (ACCT 512), a student interested in this area of concentration must take all the four listed below in Accounting.
Core Course Descriptions
| 1- ACCT 512 – Managerial Accounting | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The aim of this course is to study current issues and approaches to solving comprehensive problems in the area of managerial accounting. This course emphasizes the use of accounting information for internal planning and control purposes through readings and case studies. Some of the topics covered are Budgetary Planning, Responsibility Accounting, and Performance Evaluation through Standard Costing, Activity Based Costing, Profit Planning, Segment Reporting, Decentralization, Balanced Score Card, Target Costing and Capital Budgeting.
(Pre-Req: ACCT 531)
Elective Course Descriptions
| 1- ACCT 531 - Cost Accounting | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course provides the basic information for Management Accounting and Financial Accounting. Cost Accounting measures and reports financial and non-financial information relating to the cost of acquiring or utilizing resources in an organization. This course covers Accountant’s Role in Organizations, Introduction to Cost Terms and Purposes, Cost Volume Profit Analysis, Job Order Costing and Process Costing. It also covers how costs behave and relevant information for decision-making.
(Pre-Req: ACCT 512)
| 2- ACCT 533 - Advanced Financial Accounting | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course discusses advanced issues in the area of Financial Accounting. It helps students to advance their information through readings and case studies. It provides information about Financial Accounting Theory as well as debatable issues in this area. Some of the topics covered are accounting for Partnership, Organization and Capital Stock Transactions, Long Term Liabilities, and Consolidated Financial Statements. (Pre-Req.: ACCT 511)
| 3- ACCT 534 – Auditing | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course aims to familiarize students with Principles and Procedures of External and Internal Auditing, Auditing Standards, Ethics of the Profession, Internal Control Evaluation and Testing. Students are exposed to real cases from business life to show the effect of auditing and whether or not auditing can improve the quality of accounting reports.
(Pre-Req: ACCT 533)
| 4- ACCT 536 - International Accounting | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The aim of this course is to discuss issues from the perspective of companies that have internationalized their finance and/or operations. It also has a comparative aspect, comparing accounting across countries. It deals with harmonization of the worldwide diversity in financial reporting. This course is designed to provide students with an understanding of the significant issues in international accounting as well as provide a clear view of the work of the leading standard-setting bodies such as Financial Accounting Standard Board (FASB).

In addition to the Core Course (OPM 511), a student interested in this area of concentration must take all the four listed below in Operations Management.
Core Course Descriptions
| 1- OPM 511 - Operations Management | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This foundation course is designed for students who have not had sufficient exposure to the subject before. At the end of the course, students will have learned all the basic concepts typically taught in a first course in Operations Management. They will also have gained a working knowledge of several Operations Management techniques that are used in manufacturing and service industries. These techniques will cover such topics as production and inventory control, scheduling, project management, and quality control.
(Pre-Req.: MGT 511)
Elective Course Descriptions
| 1- OPM 531 - Global Supply Chain Management | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
International successful businesses attribute one of the major reasons for success to their strategy in Global Supply Chain Management. This Global Supply Chain Management Course provides an intensive and coordinated approach to study the flow of goods and services from raw material suppliers to the final customer. This product flow will be reviewed from a global perspective, thus providing students with a comprehensive understanding of the international business process. The increasing role-played by information flows in integrated planning and managing the supply chain will be emphasized.
(Pre-Req.: OPM 511; IBM 511)
| 2- OPM 532 - Total Quality Management | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
Students will learn how the concepts and applications of TQM are helping millions of businesses throughout the world in achieving their goals of meeting and exceeding customer requirements. Emphasis will be on studying how companies to become world-class are applying Dr. Deming’s philosophy along with the latest TQM methodologies such as Continuous Process Improvement (CPI), Six-Sigma and Lean Thinking. Students will be challenged to find opportunities to apply the concepts to local business environment.
(Pre-Req.: OPM 511)
| 3- OPM 533 - Project Management | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The objectives of this course are to provide needed skills and tools for managing variety of projects. High rates of introduction of new products, technology changes and continuous improvements make project management skills essentials for all managers. The course will focus on how to initiate, scope, plan, schedule, control and terminate a project. At the end of this, students will be able to use special techniques such as CPM and PERT and related software programs.
(Pre-Req.: OPM 511)
| 4- OPM 535 - Business Forecasting and Demand Planning | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course offers the students to acquire hands-on experience on developing and applying multi-dimensional forecasting models for use in operations management. Topics include a statistical review, data considerations, model selection, moving averages and exponential smoothing, regression analysis, time-series decomposition, Box-Jenkins (ARIMA) models, Optimal forecast combination, and forecast implementation. The students will be introduced to using software products such as SAS – widely used in Business Forecasting.
(Pre-Req.: IBM 511& MKT 511)

In addition to the Core Course (IBM 511), a student interested in this area of concentration must take all the four listed below in International Business Management.
Core Course Descriptions
| 1- IBM 511 - International Business Management | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
Students study the economic environment of business and international forces influencing the firm in order to achieve improved awareness/understanding of economic, institutional, and cultural issues pertinent to business, markets, policies, laws and trade in international business.
Elective Course Descriptions
| 1- OPM 531 - Global Supply Chain Management | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
International successful businesses attribute one of the major reasons for success to their strategy is Global Supply Chain Management. This Global Supply Chain Management course provides an intensive and coordinated approach to study the flow of goods and services from raw material suppliers to the final customer. This product flow will be reviewed from a global perspective, thus providing students with a comprehensive understanding of the international business process. The increasing role-played by information flows in integrated planning and managing the supply chain will be emphasized.
(Pre-Req.: IBM 511& OPM 511)
| 2- FIN 532 - International Finance | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course introduces the analysis of theories and practices of international finance from internal and external perspectives. It emphasizes the international monetary system, foreign exchange markets, foreign risk exposure, international banking, foreign trade financing, and the management of multinationals (MNC’s).
(Pre-Req.: IBM 511 & FIN 511)
| 3- MIS 534 - International E-Commerce | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course describes the issues related to international e-commerce and reviews the possible solutions that lead to a successful international e-commerce. Topics include Standards for International e-commerce, Security, Payment Systems and Policy issues for International e-commerce such as Taxation, Privacy, Regulation, and Law
(Pre-Req.: IBM 511 & MIS 511)
| 4- MKT 536 - Global Marketing | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The emphasis of the course is to explain how planning, implementing, and controlling marketing in the global arena is different from domestic marketing. This includes the design of the global marketing strategy, the global marketing mix, emphasizing the different international environments of global marketing, and how intercultural differences influence the international marketing strategy of international companies.
(Pre-Req.: IBM 511& MKT 511)

In addition to the Core Course (MIS 511), a student interested in this area of concentration must take all the four listed below in Management Information System.
Core Course Descriptions
| 1- MIS 511 - Management Information Systems | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The course covers the role of information systems that affect the decision-making processes and the overall organizational performance. It focuses on the characteristics and structures of management information systems, management techniques and the decision-making styles. It also covers the information systems and their relations with the organizational structures, the MIS planning, the MIS applications and other managerial aspects of information systems. Topics include Management Information Systems Types, IS Strategic Alignment, Information Intensive Business Processes, Decision Making, Telecommunication and Network, Marketing Information Systems, Human Recourse Information Systems, Accounting Information Systems and Finance Information Systems. Business Analysis Techniques Are Emphasized For Systems Such As Transactions Processing Systems (TPS), E-Business, Management Reporting Systems And Data Warehouses.
Elective Course Descriptions
| 1- MIS 531 -Database Management Systems | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course acquaints students with the techniques involved in determining database requirements, designing databases, components and architecture of databases, and database management systems. Topics will include the Context of Database Management: The Database Environment, and Development Process, Database Analysis: Modeling Data In The Organization, The Enhanced E-R Model and Business Rules, Database Design: Logical, Database Design and The Relational Model, Physical Database Design and Performance, Implementation: SQL, Advanced SQL, The Client/Server Database Environment, The Internet Database Environment, and Data Warehousing.
(Pre-Req.: MIS 511)
| 2- MIS 535 - Strategic Information Systems | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course examines the use of information technology to achieve competitive advantage, effective decision-making and efficient operations. The course will explore the usage of many kinds of information systems and technology in organizations and analyze their role, functions, and effects on competitive strategy and organizational operations.
(Pre-Req: MIS 532)
| 3- MIS 532 - Systems Analysis and Design | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
In this course, methodologies of systems analysis and design are introduced, including conducting feasibility studies, analysis, and designing application of software through the SDLC, prototyping, and rapid application development.
(Pre-Req: MIS 531)
| 4- MIS 534 - International E-Commerce | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course provides an understanding of the information technologies that enable business-to-business and business-to-consumer e-commerce while focusing on the strategic, operational, management, and societal issues associated with such technology-based commerce. In addition, topics include Standards for International e-Commerce, Security, Payment Systems and Policy Issues for International e-Commerce such as Taxation, Privacy, Regulation, and Law.
(Pre-Req: MIS 511)

In addition to the Core Courses (HRM 511 & HRM 512), a student interested in this area of concentration must take all the four listed below in Human Resource Management.
Core Course Descriptions
| 1- HRM 511 - Organizational Behavior | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course introduces the students to concepts and applications of understanding individual behavior in the work place. Various behavioral processes are also discussed such as motives, cognitive process and learning, interpersonal process: (perception, communication), small group dynamics (power, productivity, and organizational culture). The course also emphasizes work ethics and the legal environment that influences organizational behavior.
| 2- HRM 512 - Human Resource Management | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course helps firms to develop employee talent as source of competitive advantage. The course will cover strategic implications of contemporary practices in recruitment, selection, work systems, training, and compensation and performance evaluation. The course also covers the process of developing Human Resource Information System (HRIS). Also covered will be new approaches in HRM to motivate employees at the executive and worker levels. Students are expected to actively participate and contribute to the learning process by the use of case analysis and other active learning methods.
Elective Course Descriptions
| 1- HRM 531 - Human Resource Planning | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The aim of this course is to study and analyze the various methods and techniques of M.P. at the macro and micro levels. Of particular importance is the study of forces of work force supply and demand as they affect the process of Saudisation and the determination of surplus or deficit by the use of advanced quantitative models and other analytical tools.
(Pre-Req.: HRM 512)
| 2- HRM 533 - Human Resource Development | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The aim of this course is to acquaint the student with current methods of H.R. development and training. Concepts such as setting training policies, determining training needs, evaluating training outcomes, determining career paths and many others will be discussed and analyzed. The course focuses on the establishment of a balance between the individual and organizational needs.
(Pre-Req: HRM 512)
| 3- HRM 534 - Compensation Management | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The objective of this course is to introduce the student to the various approaches of Compensation Management. The concepts of equality and efficiency are fully analyzed in depth. The focus is placed on developing student’s skills in building a viable wage structure for the company based on accurate job specification and job description. Legal and ethical issues are also discussed.
(Pre-Req: HRM 512)
| 4- HRM 535 - The Legal and Ethical Environment of HRM | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The objective of the course is to study the legal environment of the firm and its effect on the various functions and processes of HRM from recruitment to retirement. The emphasis is placed on how the legal environment influences strategies and decision making of HRM. A special attention is devoted to the study of the Saudi Labor Law and its amendments. Ethical issues and work ethics are also emphasized.
(Pre-Req.: HRM 512)

In addition to the Core Course (FIN 511), a student interested in this area of concentration must take all the four listed below in Finance.
Core Course Descriptions
| 1- FIN 511 - Financial Management | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course is a broad survey of finance for all business students, which emphasize fundamental valuation concepts and their applications. It explores a set of key financial theories. The course examines theories associated with five key topics of Corporate Finance: The Efficient Market Hypothesis, Agency Theory, theories regarding the Market for Corporate Control, Capital Structure Theories, and Dividend Policy Theories.
(Pre-Req: ACCT 511)
Elective Course Descriptions
| 1- FIN 531 -Financial Planning | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course is designed for Corporate Financial Planning, Forecasting, Budgeting, Quantitative Techniques and Practices. The Importance of Ethics and the International Aspects in Financial Decision Making will be considered. The course conveys a thorough understanding of the range of Financial Management concepts that are used for planning, control and decision-making purposes by business executives, financial analysts, investors, and business owners.
(Pre-Req.: FIN 511)
| 2- FIN 532 - International Finance | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course introduces the analysis of theories and practices of international finance from internal and external perspectives. It emphasizes the International Monetary System, Foreign Exchange Markets, Foreign Risk Exposure, International Banking, Foreign Trade Financing, and The Management of Multinationals (MNC’s).
(Pre-Req: FIN 511; IBM 511)
| 3- FIN 533 - Risk Management | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
There are two specific aims associated with this course: To achieve a sound appreciation of the theory and practical aspects of Risk Management and to develop an understanding of the main theories and frameworks associated with the Management of Different Types of Risk.
(Pre-Req.: FIN 511)
| 4- FIN 534 - Security Analysis and Portfolio Management | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course introduces the Analysis of Risk and Strategies for Developing Efficient Portfolios; Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Stocks and Fixed Income Securities, Theories, and Techniques of Security Valuation; Examination of Securities Markets and Interest Rate Behavior in the Context of National and International Economic Trends.
(Pre-Req.: FIN 511)

In addition to the Core Course (MKT 511), a student interested in this area of concentration must take all the four listed below in Marketing.
Core Course Descriptions
| 1- MKT 511 - Marketing Management | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The objective of the course is to provide a clear picture of the marketing concepts and practice. It includes the major activities in managing marketing strategy and the marketing mix; including marketing analysis, planning, implementation, and control.
Elective Course Descriptions
| 1- MKT 531 - Consumer Behavior | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The objective of the course is to examine and understand how consumers make decisions to spend their available resources on consumption-related items. Concepts developed in other scientific disciplines such as psychology, sociology, social psychology, anthropology, and economics are presented to explain consumer behavior. In addition, it includes the personal, social and cultural influences on consumer behavior; including opinion leadership, reference groups, family, and culture.
| 2- MKT 532 - Marketing Research | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The objective of the course is to provide the students with the required research skills to conduct marketing research. The emphasis is on the different steps of the marketing research process including defining the research problem, the research design, and methods to collect the required data, selecting the sample, analyzing data, and how to prepare and present the research results, conclusion and recommendations.
(Pre-Req.: MKT 511 & MGT 511)
| 3- MKT 535 - Strategic Marketing Management | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The objective of this course is to help improve the effectiveness of marketing practice. So this course emphasizes making the student aware of the major aspects of the planning and controlling of marketing operations; locating marketing planning and control within a strategic context; demonstrating how analytical models and techniques might be applied to marketing planning and control to produce more superior marketing performance; and giving full recognition to the problems of implementation and how these problems might be overcome.
(Pre-Req.: MGT 581)
| 4- MKT 536 - Global Marketing | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The emphasis of the course is on explaining how planning, implementing, and controlling marketing in the global arena is different from domestic marketing. This includes the design of the global marketing strategy, the global marketing mix, emphasizing the different international environments of global marketing, and how intercultural differences influence the international marketing strategy of international companies.
(Pre-Req.: IBM 511& MKT 511)

This section of the program is carefully designed to accommodate MBA seekers, who come from non-business background. The fact that such students need a kind of survival kit that helps them to cope with their peers who come from business background or hold an undergraduate degree in business related discipline. This kit is the Pre-MBA program, which comprises 6 courses, 3-credits each and will be offered in one semester. Applicants who have accredited background in one or more of these courses may get a waiver on case-to-case basis.
| Pre-MBA Course List | |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Quantitative Business Analysis | 3 credits |
| Principles of Accounting | 3 credits |
| Principles of Finance | 3 credits |
| Principles of Economics | 3 credits |
| Introduction to Management Information Systems | 3 credits |
| Principles of Management | 3 credits |
| 1- MGT 499 – Introduction to Quantitative Business Analysis | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
Quantitative Business Analysis is a required course designed to prepare MBA students with a set of tools to meet the challenges of today’s business environment. This course is about statistics and basic modeling for management decisions.
It covers various topical areas spanning from descriptive statistics to inferential statistics and introduction to mathematical programming.
The objectives are:
| 2- ACCT 499 – Principles of Accounting | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The aim of this course is to familiarize students with the essential accounting system terminologies and functions.In this course, students review accounting reports and methods. The course focuses on the preparation of financial statements.
Emphasis is placed also on the interpretation and use of financial statements for decision making as well as steps of accounting cycle.
| 3- FIN 499 - Principles of Finance | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course aims to set the basic financial background that supports the financial knowledge and skills needed for studying MBA courses.
Course topics will cover the basics of financial management and financial markets and institutions.
In addition, teaching the accounting and financial statements and how to use them in evaluating the firm’s financial performance are included. Furthermore, the course will focus on the concepts of the time value of many and the meanings and measures of risk and return.
| 4- Econ 499 – Principles of Economics | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course aims to set the basic economic background that supports the economic knowledge and skills needed for studying MBA courses.
Microeconomics concepts will cover demand, supply and equilibrium in addition to elasticity and consumer theory. Microeconomics will focus too, on the theory of the firm, competition and monopoly. The student will learn about wages, interest, rent and profit as returns of the economic factors.
Macroeconomics will cover the national income accounting and determination, unemployment, inflation, money and banking and public expenditure and finance. Macroeconomics will focus too, on international trade and protection, the balance of payment and exchange rates in addition to the concepts of managing the economy.
| 5- BUS 499 – Principles of Management | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course focuses on the key managerial functions: planning, organizing, staffing, directing and controlling. Particular emphasis is given to design and development of organizations, marketing decisions, and labor management relations, financing decisions, management theory and role of management information system. The course also introduces students to the main functions of enterprise as well as business environment. Ethics and Social responsibility are also addressed.
| 5- MIS 499 – Introduction to Management Information System | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course is an introduction to information systems and information technology for students who are or who will become business professionals in the fast changing business world of today. The focus is helping students learn how to use and manage information technologies to revitalize business process, improve business decision making and gain competitive advantages. There is a major emphasis on the essential role of internet technologies in providing a platform for business, commerce and collaboration process among all business stakeholders in today has networked enterprises and global markets.

Qualified applicants will be informed of their acceptance. Full Acceptance is issued to those who submitted and fulfilled all requirements. Conditional acceptance for those who did not fulfil the specific documentation criteria. Applicants who finished a degree with non-business background are required to take the Pre-MBA courses.
Admission to the MBA program will not be considered official until the application file is complete. No amount of credit taken while on Unclassified Status will assure a student of full admission. A letter from the MBA Executive Director will confirm admission.
Applicants who do not meet some of the above requirements can apply and conditional admission may be granted.
Graduate Honors record not available...
Graduate Honors record not available...
Graduate Honors record not available...
1. Bachelor’s degree from a local and international College/University recognized by MOE.
2. Grade Point Average (GPA) of 2.25, or higher on a 4.0 Scale, 3.25, or higher on a 5.0 Scale in previous university work or equivalent.
3. The applicant must have graduated within the past 10 years. The Admission Committee has the right to exempt a student from this condition on a case-to-case basis.
4. An official transcript that clearly indicates the completion of a bachelor’s degree must be submitted to the Admission Office. If a student completed a course at another college or university, official transcripts also should be submitted. If a degree is obtained outside the KSA, Saudi nationals should equalize their degree from MOE and for Non-Saudi the degree must be attested by the Saudi Embassy at the country of origin and from the Ministry of Foreign Affairs in Jeddah, KSA.
5. After the verification of all the documents submitted by the student, the student must have a personal interview with the Admission Committee to complete the admission procedures.
6. Additionally, the degree must be within 10 years of graduation from the date of applying to the MEM program..
7. Preferably one (1) year of professional experience..
8. Letter of Purpose (250 words minimum).
9. All students are required to obtain a minimum TOEFL/IELTS score of:.
a. 67 on an internet-based test (IBT).
b. 6.0 on an IELTS Examination.
The above condition of English language proficiency will be waived if the student graduates from a school with English as the medium of instruction. The student should secure a certification stating that the degree was conducted in English or upon the acceptance of the interview committee when showing a competency level in English.
10. Two letters of nomination and recommendation from senior Engineering associates that objectively assess the applicant’s strengths, weaknesses, potential, and suitability for the MEM program are required.
11. Submit a statement of intent outlining personal short-term and long-term career goals, reasons for applying for the program, and explain how the program will help achieve these goals in addition to an identification letter from the employer, if any.
12. A completed Application for Admission Form with a SAR 1000 non-refundable application fee made payable to the College of Business Administration must be submitted to the College of Engineering-MEM Program Admissions Office.
Qualified applicants will be informed of their acceptance. Full Acceptance is issued to those who submitted and fulfilled all requirements. Conditional acceptance for those who did not fulfill the specific documentation criteria. Applicants who finished a degree with a non-business background are required to take the Pre-MEM courses.
Admission to the MEM program will not be considered official until the application file is complete. No amount of credit taken while on Unclassified Status will assure a student of full admission. A letter from the General Director for Graduate Studies confirms admission.
Applicants who do not meet some of the above requirements can apply and conditional admission may be granted.
For students with non-Industrial Engineering backgrounds, our MEM program acts as a tool to guide them throughout their careers, filling gaps in knowledge to move forward and take the next step within their current organization or opening doors for development and progress in a new direction. Our MEM Program provides a comprehensive Industrial Engineering grounding, it creates opportunities for students from virtually any background. Accordingly, the College of Engineering has designed a number of Pre-MEM Courses to accommodate MEM applicants from this category.
The 12-credit Pre-MEM minor is a fast track for any undergraduate non-Industrial Engineering major who wants to continue his/her studies and earn a Master of Engineering Management (MEM) at The University of Business and Technology, College of Engineering. The courses serve as a foundation for the MEM program and can be credited to the bachelor’s degree according to the requirements of his degree or college.
Pre-MEM Courses are also open for Non-credit applicants seeking Industrial Engineering knowledge for knowledge according to the availability of slots.
Attendance in these courses is vital since the students attending the classes will be granted an “Attendance Certificate” without numerical grading or credits.
Students transferring from another accredited institution recognized by the Saudi Ministry of Education (MOE) may be eligible to transfer a maximum of 9 credits of graduate coursework for courses already successfully completed with an average of (B) or 3.75/5 for each. The MEM Admission Committee will determine the eligible transfer credits of each student. Only grades in the courses taken in the College of Engineering will appear on the MEM transcript and be counted toward the GPA.
Requirement of Courses of Equalization:
• Courses from an accredited university under MOE.
• B grade or higher in the course(s) to be equalized.
• Official transcript, Course description, contents, and objectives must be at least equivalent to 75% of the corresponding course at MEM.
• Credit hours for the course should be equal to 3 credit hours.
• Equalized courses at MEM are assigned a grade of T prefix (meaning transfer). These grades are not counted as part of the student’s accumulated GPA.
• Preparatory and vocational courses are not considered for equalization of any courses at the College of Engineering.
• The validity of any courses to be equalized is 2 years.
1. All students who want to register must go to Opera online.
2. Late registration starts on the first day of the beginning of classes according to the college academic calendar of the semester and finishes on the last day for adding courses.
3. A maximum of 12 credit hours can be registered in one semester for full-time students and 6 credit hours for part-time ones.
4. Students should follow and respect timetables of registration, add, drop, and withdraw according to the college academic calendar.
5. Registering students must follow course pre-requisite conditions.
6. All forms of drop, add, late registration and withdrawals should be presented to the Finance Department for financial review.
7. Registration steps are:
• Pay your fees
• Register online
Students may add or drop courses without any penalties during the first 2 weeks of each term. An Add/Drop Form needs to be completed by the student in the MEM Registrar’s office or online if available. This form must be signed by both the course instructor and the student and returned to the Registrar’s office for processing.
Students who wish to attend scheduled classes but not to earn credits can be permitted after the approval of the General Director for Graduate Studies.
A student may withdraw from a course up until the end of the 14th week of the term without academic penalty. It will be shown as a “W”, withdraw, on his/her transcript. After week 14 of the term elapsed, all students will be awarded grades for their registered courses based on their assessment.
The maximum number of credit hours allowed to be taken in an academic semester is 12 credit hours, while the minimum credit hours allowed to be registered is 6 credit hours. However, graduating students can register for 15 credit hours maximum in their last semester if their GPA is 4.5 or above.
In order to prepare for our MEM Program, it would be helpful to have taken classes in Engineering Economy, Operation Research, Engineering Statistics and Production Planning and Control. The number of courses required from this category differs from an applicant to another according to the degree of relevance of his/her education and area of expertise to the field of Underground.
| The Pre-MEM Course List | Credits |
|---|---|
| Engineering Economy | 3.00 |
| Operation Research | 3.00 |
| Engineering Statistics | 3.00 |
| Production Planning and Control | 3.00 |
Core & General Courses: (7 Courses, 21 Credit hours)
Regardless of the MEM option, all students are required to complete the following courses:
| COURSE | Course Title | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Core courses in Engineering Management | ||
| ENGM 510 | Advanced Engineering Statistics | 3 |
| ENGM 515 | Advanced Engineering Economy | 3 |
| ENGM 520 | Quality and Performance Management | 3 |
| ENGM 530 | Concepts and Principles of Engineering Management | 3 |
| 540 | Production/Operations Management | 3 |
| ENGM 550 | Project Management | 3 |
| ENGM 560 | Safety Engineering | 3 |
| Sub-Total | 3 | |
| Core courses in Business Administration | ||
| ACCT 532 | Managerial Accounting | 3 |
| ACCT 532 | Human Resources Management | 3 |
| Sub-Total | 6 | |
Areas of Concentration (2 courses, 6 hours)
The MEM program is designed to include 3 option areas to cater different interests of the professional students. For the option areas, student is required to select 2 courses under the option area selected.
| MEM Option Areas (Elective Courses) | Credits |
|---|---|
| Construction Management | 6.00 |
| Industrial Management | 6.00 |
| Quality Management | 6.00 |
MEM Option Areas (Elective Courses):
In addition to the 9 core courses of the program, 2 courses must be taken to complete the option credits to qualify student for graduation in the MEM degree with option.
Grading is one of the primary means of communicating the student’s performance and level of understanding of the subject matter. For the purpose of communicating the level of performance achieved, the following grades have been adopted:

In rare instances, students may not be able to finish all work-related materials in order for the faculty to award a grade. In these instances, a grade of IC may be issued. All IC grades must be changed no later than the end of the following term or they automatically convert to a grade of ‘’F’’.

MEM students who have earned at least 90% of their total credits at COLLEGE of Engineering-MEM program and do not have any grade of “C” is awarded the following honors:
Honors are indicated on the student’s Official Transcript of Records and diploma.
| 1- ACCT 532 – Managerial Accounting (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The aim of this course is to study current issues and approaches to solving comprehensive problems in the area of managerial accounting. This course emphasizes the use of accounting information for internal planning and control purposes through readings and case studies. Some of the topics covered are Budgetary Planning, Responsibility Accounting, Performance Evaluation through Standard Costing, Activity Based Costing, Profit Planning, Segment Reporting, Decentralization, Balanced Score Card, Target Costing and Capital Budgeting. Prerequisite: ENGM 515
| 2- HRM 510 - Human Resources Management (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course helps firms to develop employee talent as source of competitive advantage. The course will cover strategic implications of contemporary practices in recruitment, selection, work systems, training, and compensation and performance evaluation. The course also covers the process of developing Human Resource Information System (HRIS). Also covered will be new approaches in HRM to motivate employees at the executive and worker levels. Students are expected to actively participate and contribute to the learning process by the use of case analysis and other active learning methods. Prerequisite: ACCT 532
Construction Management:
Choose a concentration area (two courses in one chosen area) from the following. Note that the Construction Management concentration area has three courses from which the student has to select two courses.
Pre-requisite for Area of concentration I is ENGM 520
Pre-requisite for Area of concentration II is ENGM 560
| 1- ENGM 570: Construction Scheduling and Cost Estimating (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
A study of planning and scheduling techniques including Gantt Charts, CPM, PERT, time-cost tradeoffs, and resource scheduling under constraints. Project control and Work-Breakdown-Structure (WBS) concepts will also be covered. At the completion of this course, students will be able to develop a WBS for a construction project, develop scheduling activities needed for constructing a project, and develop a project control system to monitor the progress of a project. This course will also cover the procedures involved in material quantity takeoffs and in estimation of labor, material, equipment, and overhead costs. The course will also discuss bidding procedures and elements of construction cost control. Prerequisite: ENGM 520
| 2- ENGM 571: Contract Management and Project Delivery System (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course will explore the contract management process in three broad phases: pre-award, contract award and post-award. Each step of the phases will be addressed from both the Buyer and Seller perspectives, in both the government and commercial environments. Coverage of the standard contracts between various agencies involved in construction is provided in this course. Analysis of traditional and current project delivery methodologies is presented. Advanced topics covering FIDIC conditions, arbitration, legal aspects, Saudi building codes, and procurement management is provided. Issues related to insurance and bonding in the construction industry are highlighted. Students will participate in realistic team exercises to enhance their contracting skills, to include mock negotiations, dispute resolution and oral proposals. Prerequisite: ENGM 560
| 3- ENGM 572: Construction Risk Management (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course will provide project managers with the necessary knowledge and tools needed for identifying, analyzing, and managing the risks associated with construction project management. Prerequisite: ENGM 520 or ENGM 560
Pre-requisite for Area of concentration I is ENGM 520
Pre-requisite for Area of concentration II is ENGM 560
| 4- ENGM 580: Organizational Change Management (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course shares modern applications of organizational change techniques in engineering management settings. Students draw from classic and current readings and relevant case studies to scope and analyze their own case studies. (See ABET course syllabus in the Appendix for a sample list of readings for this course.) Prerequisites: ENGM 520
| 5- ENGM 581: Systems Engineering (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The student will learn the fundamental systems engineering methodologies. This course provides the tools and methodology to design solutions that more effectively meet customer requirements. The course has an applied focus around a project performed by small teams. The systems engineering approach is disciplined, yet considers the customer needs first and foremost. Prerequisites: ENGM 560
Quality Management:
Pre-requisite for Area of concentration I is ENGM 520
Pre-requisite for Area of concentration II is ENGM 560
| 6- ENGM 590: Quality Control (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course presents topics in quality control and total quality management. Use of methods and recent developments in quality control are covered. Statistical methods used in controlling process variation receive emphasis. Prerequisite: ENGM 520
| 7- ENGM 591: Reliability Engineering (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course presents the managerial and mathematical principles and techniques of planning, organizing, controlling, and improving the reliability functions of an organization. This includes the formulation of mathematical models for reliability allocation and redundancy, time dependent and time independent prediction measures for both maintained and non-maintained systems. Emphasis is on practical applications for product or system design. Prerequisite: ENGM 560
Irrespective of area of concentration, students must choose only TWO courses from the following Elective courses: Prerequisite for Approved Technical Elective I : ENGM 540 Prerequisite for Approved Technical Elective II : ENGM 540, ACCT 532.
In addition to any other pre-request mentioned below.
| 1- MKT 510: Marketing Management (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The objective of the course is to provide a clear picture of the marketing concepts and practice. It includes the major activities in managing marketing strategy and the marketing mix, including marketing analysis, planning, implementation, and control. Prerequisite: ENGM 540,
| 2- FIN 511: Financial Management (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course is a broad survey of finance for all business students which emphasizes fundamental valuation concepts and their applications. It explores a set of key financial theories. The course examines theories associated with five key topics of Corporate Finance: The Efficient Market Hypothesis, Agency Theory, theories regarding the Market for Corporate Control, Capital Structure Theories, and Dividend Policy Theories. Prerequisite: ENGM 540, ACT 511
| 3- EPR 510: Entrepreneurship (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This interdisciplinary course focuses on all aspects of starting a new business with emphasis on the critical role of recognizing and creating opportunities. Topics include Attributes of Entrepreneurs and Entrepreneurial Careers, Evaluating Opportunities, Writing Business Plans, and Venture Financing. Prerequisite: ENGM 540, ACCT 532
| 4- IBM 511: International Business Management (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
Students study the economic environment of business and international forces influencing the firm in order to achieve improved awareness/understanding of economic, institutional, and cultural issues pertinent to business, markets, policies, laws and trade in international business. Prerequisite: ENGM 540,
| 5- MIS 510: Management Information Systems (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The course covers the role of information systems that affect the decision making processes and the overall organizational performance. It focuses on the characteristics and structures of management information systems, management techniques and the decision-making styles. It also covers the information systems and their relations with the organizational structures, the MIS planning, the MIS applications and other managerial aspects of information systems. Topics include Management Information Systems Types, IS Strategic Alignment, Information Intensive Business Processes, Decision Making, Telecommunication and Network, Marketing Information Systems, Human Resource Information Systems, Accounting Information Systems and Finance Information Systems. Business analysis techniques are emphasized for systems such as Transactions Processing Systems (TPS), E-Business, Management Reporting Systems and Data Warehouses. Prerequisite: ENGM 540
| 6- MGT 581: Business Strategies (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
This course investigates the methods and techniques used to formulate competitive strategy through the analysis of industries, competitive dynamics, the general management process, and the achievement of sustainable competitive advantage. Students will also be exposed to growth strategies, comparative management, impact of taxation, technology strategies; product development and new market strategies. The course heavily emphasizes the use of case studies and in-class simulations. Prerequisites: ENGM 515, FIN 511, MKT 511, MIS 511 & OPM 511 (ENGM 540)
| 7- HRM 536: Cultural Diversity in Business (3) | Credits 3.00 |
|---|
The course introduces students to the role communication plays in shaping interactions between members of differing cultural groups. It includes an introduction to anthropology through the comparative study of cross cultures and how differences affect running the business. The course also covers obstacles and solutions in dealing with workforce diversity pertaining to the Saudi business environment. An emphasis will be made to Inter-Cultural Studies through the examination of:
| 1- ENGM 255 – Engineering Economy | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
Fundamentals of engineering economy. Time value of money. Evaluation of alternatives. Replacement and retention analysis. Break even analysis. Depreciation methods. Basics of inflation.
| 2- ENGM 311 – Operations Research | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
Introduction to Operations Research. Formulation of linear programming problems. Graphical solution. The Simplex algorithm. Duality and sensitivity analysis. Transportation and assignment problems. Integer and Goal programming.
| 3- ENGM 332 – Engineering Statistics | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
Basic notions of statistics applicable to engineering problems. Moment generating functions. Random samples and sampling distributions. Parameter estimation. Hypothesis testing. Nonparametric tests. Simple and multiple regression.
| 4- ENGM 451 – Production Planning and Control | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
Basic concepts of Production and Operations Management (POM). Design of products and services. Processes and technologies. E-commerce and operations management. Inventory management. Supply-Chain management. Just-in-time and lean production. Forecasting. Material Requirements Planning (MRP). Introduction to Enterprise Requirement Planning (ERP). Capacity and aggregate planning. Scheduling.
MEM Course Descriptions
MEM Engineering Management Core Course Descriptions
| 5- ENGM 510: Advanced Engineering Statistics (3) | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
This course covers both the foundations for statistical reasoning and statistical applications related to business and engineering decision-making. Topics include descriptive and inferential statistics, regression, analysis of variance, and design of experiments. Prerequisite: ENGM 332
| 6- ENGM 515: Advanced Engineering Economy (3) | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
Application of the principles of engineering economy for the establishment of equipment and system feasibility. Concepts, principles, and techniques for making decisions pertaining to the acquisition and retirement of capital goods by industry and government. Topics also include: interest, equivalence, taxes, depreciation, uncertainty and risk, incremental and sunk costs, and replacement models. Prerequisite: ENGM 255
| 7- ENGM 520: Quality and Performance Management for Engineers (3) | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
This course teaches the practicing engineer how to enhance the quality and performance characteristics of organizational systems. Quality and performance management requires a firm understanding of fundamentals, theory-based models, broadly-implemented initiatives such as Lean Six Sigma, kaizen, and lean techniques, and global quality standards; and how to build a quality and performance improvement system. Prerequisite: ENGM 510
| 8- ENGM 530: Concepts and Principles of Engineering Management (3) | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
This course examines the concepts, models, and applications of organizational behavior in engineering management settings. Students will learn to analyze the role of human behavior in complex sociotechnical systems. Prerequisite: Graduate Standing
| 9- ENGM 540: Production/Operations Management (3) | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
Topics relating to the planning and control functions of manufacturing systems are presented. These topics include management of the production system, strategies of product design and process selection, design of production systems, plant location, shop floor control, purchasing, quality management, and productivity improvement. Prerequisite: ENGM 451
| 10- ENGM 550: Project Management (3) | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
This course provides a foundation in project management techniques, models, and knowledge to enable to student to design and operate an effective project management system. The engineer’s approach to problem-solving is highlighted in the context of managing projects. The project manager role is explicated for interactions with team members, leadership, and other stakeholders. Topics are aligned with the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK). Prerequisite: ENGM 530
| 11- ENGM 560: Safety Engineering (3) | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
A study of the technical fundamentals and management of safety and hazards associated with industrial processes. Topics include fires and explosions, relief systems, hazard identification, risk assessment, hazardous waste generation, toxicology, case studies, oil and gas industry safety, construction safety, and regulatory requirements. Prerequisite: Graduate Standing
| 12- ENGM 595 Case Study Report (3) | Credits 1.00 |
|---|
This course is designed to be taken during the last semester culminating all aspects of engineering management in the chosen area of concentration. This is an open ended, practical, Industry-oriented, special problems of interest under the direction of a faculty member in the chosen area of concentration. Projects will involve systems design, analysis and applications. Prerequisite: HRM 510, ENGM 311
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| ENGM255 | ENGINEERING ECONOMY | 1 |
| ENGM332 | ENGINEERING STATISTICS | 1 |
| ENGM451 | PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL | 1 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| ENGM520 | QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ENGM540 | PRODUCTION/OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ENGM550 | PROJECT MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ACCT532 | MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING | 3 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| HRM 510 | HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ELCTG1 | TECHNICAL ELECTIVES | 3 |
| ELCTME1 | AREA OF CONCENTRATION I | 3 |
| ELCTME2 | AREA OF CONCENTRATION II | 3 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| ENGM595 | CASE STUDY REPORT | 3 |
| ELCTG2 | TECHNICAL ELECTIVES | 3 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| ENGM255 | ENGINEERING ECONOMY | 1 |
| ENGM332 | ENGINEERING STATISTICS | 1 |
| ENGM451 | PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL | 1 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| ENGM520 | QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ENGM540 | PRODUCTION/OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ENGM550 | PROJECT MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ACCT532 | MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING | 3 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| HRM 510 | HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ELCTG1 | TECHNICAL ELECTIVES | 3 |
| ENGM570 | CONSTRUCTION SCHEDULING AND COST ESTIMATING | 3 |
| ENGM571 | CONTRACT MANAGEMENT AND PROJECT DELIVERY SYSTEM | 3 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| ENGM595 | CASE STUDY REPORT | 3 |
| ELCTG2 | TECHNICAL ELECTIVES | 3 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| ENGM255 | ENGINEERING ECONOMY | 1 |
| ENGM332 | ENGINEERING STATISTICS | 1 |
| ENGM451 | PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL | 1 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| ENGM520 | QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ENGM540 | PRODUCTION/OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ENGM550 | PROJECT MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ACCT532 | MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING | 3 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| HRM 510 | HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ELCTG1 | TECHNICAL ELECTIVES | 3 |
| ENGM570 | CONSTRUCTION SCHEDULING AND COST ESTIMATING | 3 |
| ENGM571 | CONTRACT MANAGEMENT AND PROJECT DELIVERY SYSTEM | 3 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| ENGM595 | CASE STUDY REPORT | 3 |
| ELCTG2 | TECHNICAL ELECTIVES | 3 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| ENGM255 | ENGINEERING ECONOMY | 1 |
| ENGM332 | ENGINEERING STATISTICS | 1 |
| ENGM451 | PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL | 1 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| ENGM520 | QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ENGM540 | PRODUCTION/OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ENGM550 | PROJECT MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ACCT532 | MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING | 3 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| HRM 510 | HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ELCTG1 | TECHNICAL ELECTIVES | 3 |
| ENGM570 | CONSTRUCTION SCHEDULING AND COST ESTIMATING | 3 |
| ENGM571 | CONTRACT MANAGEMENT AND PROJECT DELIVERY SYSTEM | 3 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| ENGM595 | CASE STUDY REPORT | 3 |
| ELCTG2 | TECHNICAL ELECTIVES | 3 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| ENGM255 | ENGINEERING ECONOMY | 1 |
| ENGM332 | ENGINEERING STATISTICS | 1 |
| ENGM451 | PRODUCTION PLANNING AND CONTROL | 1 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| ENGM520 | QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ENGM540 | PRODUCTION/OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ENGM550 | PROJECT MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ACCT532 | MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING | 3 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| HRM 510 | HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT | 3 |
| ELCTG1 | TECHNICAL ELECTIVES | 3 |
| ENGM570 | CONSTRUCTION SCHEDULING AND COST ESTIMATING | 3 |
| ENGM571 | CONTRACT MANAGEMENT AND PROJECT DELIVERY SYSTEM | 3 |
| Course Code | Course Name | Units |
|---|---|---|
| ENGM595 | CASE STUDY REPORT | 3 |
| ELCTG2 | TECHNICAL ELECTIVES | 3 |
The finance department serves the students from initial entry to final march to graduation in the two-year Master of Engineering Management (MEM). All financial matters are transacted in this office specifically the collection of the required school fees:
New students can pay the first time to the University cashier. All students can pay tuitions through the special Bank account that is given to them through their OPERA ONLINE accounts. They also can pay to the University cashier or by credit card through visa etc.
In case of a pre-registration, a student is required to pay 25% of the total value of the courses registered at the time of registration. The other 25% due for the semester is due at the start of ordinary registration period.
Note: For furthermore any information regarding finance and payments.
Please contact:
Mr. Moaad Jamil Fakerha.
Email: moaad@UBT.EDU.SA
Tel: 012- 2159120
Program Description:
Unlike the M.Sc. program, which offers a broad understanding of the cross-functional areas of business, the M.Sc. in Finance provides more detail and a greater depth of understanding of contemporary financial theory, practices and applications. Students will learn how to develop and apply effective financial decision-making techniques associated with raising and investing capital. The program will culminate with the completion of an applied business research project.
Program Description:
Unlike the M.Sc. program, which offers a broad understanding of the cross-functional areas of business, the M.Sc. in Marketing provides more detail and a greater depth of understanding of contemporary marketing theory, practice and application. Students will learn how to develop and apply effective marketing techniques and approaches to a variety of business situations. The program will culminate in the development of a marketing plan for an existing or proposed business and a final presentation of the plan before faculty and business leaders.
Program Description:
The M.Sc. in Accounting provides students with an in-depth study of different functional areas of accounting, which will prepare students for various professional accounting careers.
Program Description:
The Masters of Science in Human Resource Management at the UBT is designed to provide an optimal mix of advanced knowledge and contemporary H.R practices necessary for professionals to move into senior H.R roles and execute human capital strategy to help their businesses better compete in the market place.
Program Description:
The M.Sc. in Supply Chain Management prepares graduates to assume managerial and leadership roles in the industrial or service sectors of the Saudi economy and act as a driving force to increase the competitive advantage for their organizations thereby contributing directly to the CBA’s mission to develop successful leaders for the local and global business environments.

This section of the program is carefully designed to accommodate MBA seekers, who come from non-business background. The fact that such students need a kind of survival kit that helps them to cope with their peers who come from business background or hold an undergraduate degree in business related discipline. This kit is the Pre-MBA program, which comprises 6 courses, 3-credits each and will be offered in one semester. Applicants who have accredited background in one or more of these courses may get a waiver on case-to-case basis.
The finance department serves the students from initial entry to final march to graduation in the two-year Master of Engineering Management (MEM). All financial matters are transacted in this office specifically the collection of the required school fees:
Recognizing that attending the MEM Program of the COLLEGE of Engineering is a significant investment of time and money, we strive to provide our students with various means to finance the degree. Total tuition cost of the Two-Year Program is approximately SAR 132,702. Tuition is set by the University’s Board of Trustees and is ratified each year.
The cost of each semester varies depending on the number of units taken. Students will not be allowed to register any credit hours unless payment is received in full (40% is accepted).
New students can pay the first time to the University cashier. All students can pay tuitions through the special Bank account that is given to them through their OPERA ONLINE accounts. They also can pay to the University cashier or by credit card through visa etc.
The full-time MEM student has 4 academic terms. Tuition is charged per term. Payments may be made by bank draft, electronic fund transfer through the student given (IBAN) at the Saudi French Bank (Banque Saudi Fransi) or Cash. Program tuition is due in three instalments as follows:
50% At the beginning of each term
In case of a pre-registration, a student is required to pay 25% of the total value of the courses registered at the time of registration. The other 25% due for the semester is due at the start of ordinary registration period.
Note: For furthermore any information regarding finance and payments.
Please contact:
Mr. Moaad Jamil Fakerha.
Email: moaad@UBT.EDU.SA
Tel: 012- 2159120
50% At the beginning of each term
Semester grade reports are not mailed to students. Semester final grades are typically available through OPERA approximately one week after the close of the semester. Students may view their grades by logging onto OPERA.
Is a temporary grading which describes the excused inability of a student to complete the course requirement at the decided time and it is usually shown by the letters (IC). It is not calculated in the grade point average.
It is the average of the total points of all academic units divided by the number of credit hours for the specific semester. Points are calculated by multiplying each academic unit by its corresponding weight of points.
It is the average of total points divided by the number of credit hours for all completed credit hours by a student for all semesters.
Unlike the MBA program, which offers a broad understanding of the cross-functional areas of business, the M.Sc. in Finance provides more detail and a greater depth of understanding of contemporary financial theory, practices and applications. Students will learn how to develop and apply effective financial decision-making techniques associated with raising and investing capital. The program will culminate with the completion of an applied business research project.

Unlike the MBA program, which offers a broad understanding of the cross-functional areas of business, the M.Sc. in Marketing provides more detail and a greater depth of understanding of contemporary marketing theory, practice and application. Students will learn how to develop and apply effective marketing techniques and approaches to a variety of business situations. The program will culminate in the development of a marketing plan for an existing or proposed business and a final presentation of the plan before faculty and business leaders.

The M.Sc. in Accounting provides students with an in-depth study of different functional areas of accounting, which will prepare students for various professional accounting careers.

The Masters of Science in Human Resource Management at the UBT is designed to provide an optimal mix of advanced knowledge and contemporary H.R practices necessary for professionals to move into senior H.R roles and execute human capital strategy to help their businesses better compete in the market place.

The M.Sc. in Supply Chain Management prepares graduates to assume managerial and leadership roles in the industrial or service sectors of the Saudi economy and act as a driving force to increase the competitive advantage for their organizations thereby contributing directly to the CBA’s mission to develop successful leaders for the local and global business environments.
