Welcome To JCA
Jeddah College of Advertising (JCA) is the third college to be established at the University of Business and Technology (UBT). JCA works within the general objectives of the university: “Education for Job Opportunities and Entrepreneurship”. The college existed as a result of the fruitful collaboration and affiliation between Buckinghamshire New University in the United Kingdom at UBT. The general purpose of JCA is to provide students in Saudi Arabia and the surrounding countries with the opportunity to study advertising and its related fields in international programs that focus on hands-on applications and training rather than only theoretical study. Although the study programs in JCA are equivalent to those being taught in the best universities in the UK, they have been scientifically modified to accommodate the Saudi Education System.












.jpg)









---FINAL-EXAMS-SCHEDULE-FALL-2020.png)
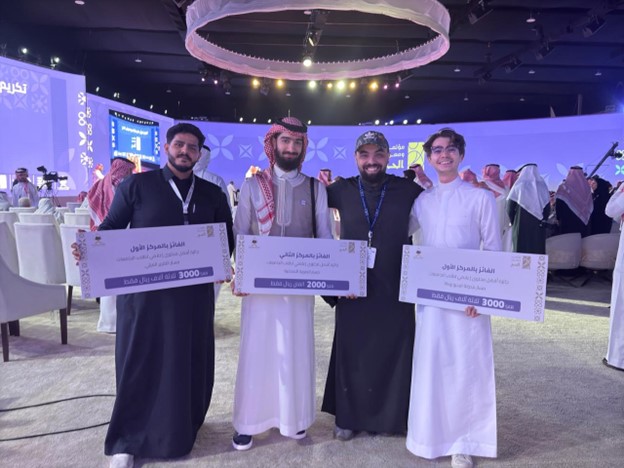
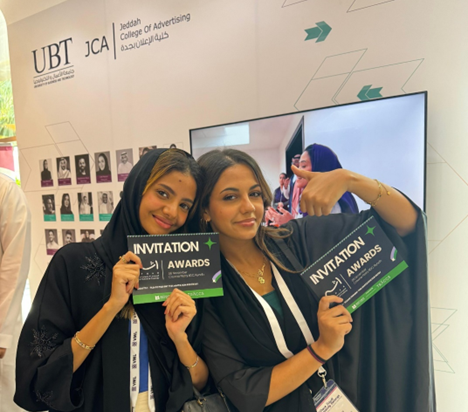
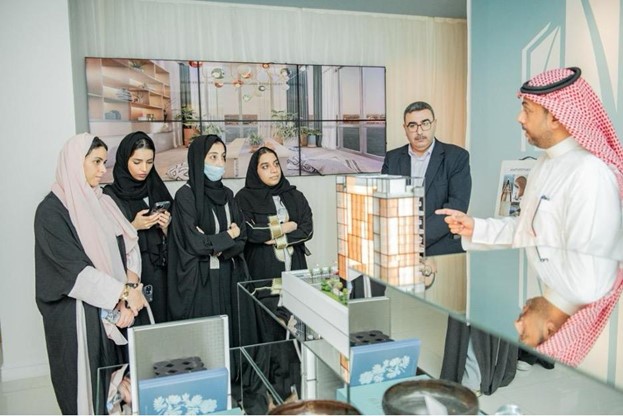
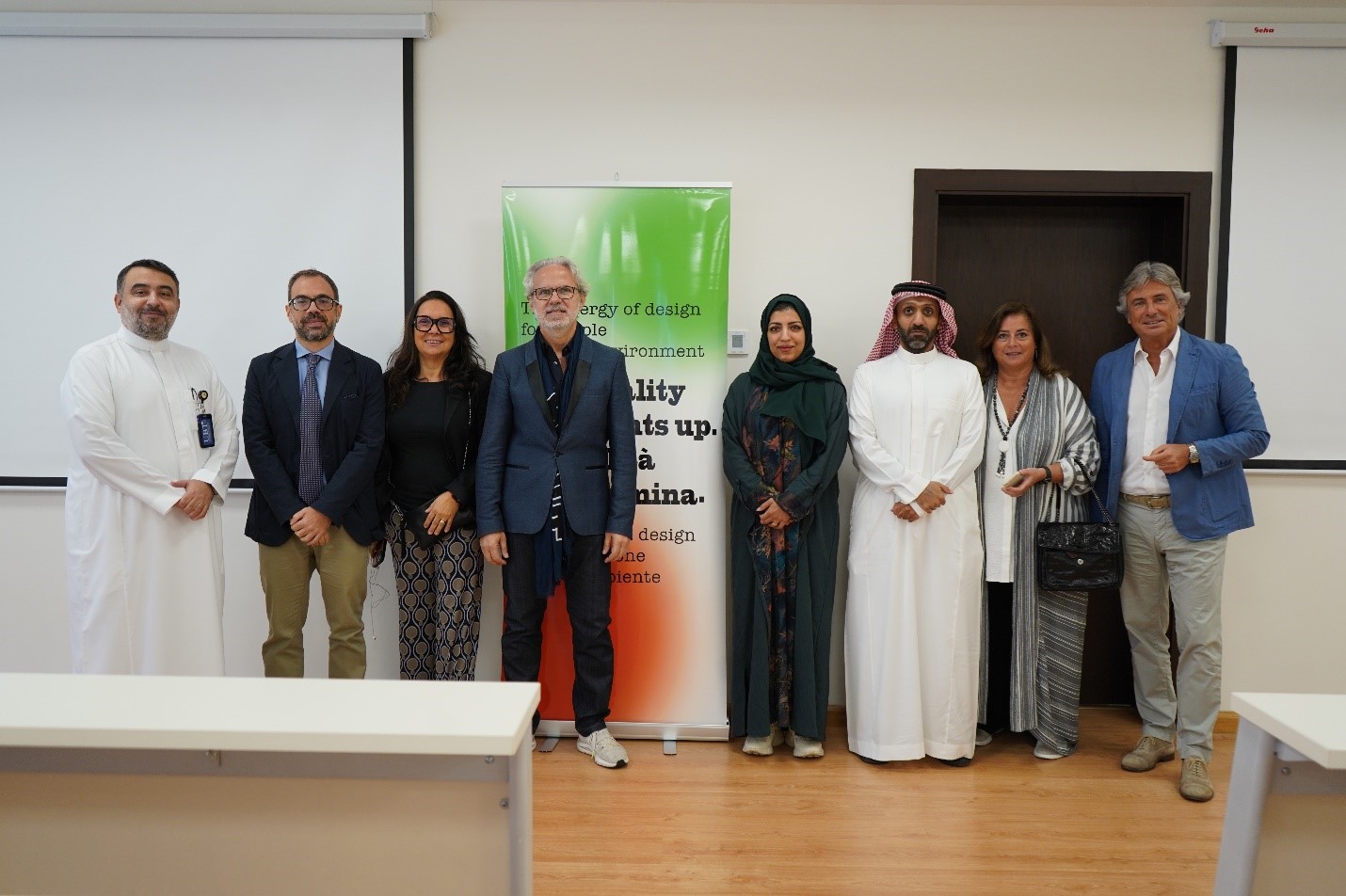

























































SOCIAL MEDIA